Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
What
is the name of the element with the symbol Pb? a. | iron | b. | lead | c. | phosphorus | d. | plutonium | e. | rubidium | | |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which
of the following substances is not an element?
|
|
|
3.
|
A
pure substance that is composed of two or more different elements is a. | a chemical
compound. | b. | a multi-element. | c. | an
atom. | d. | a heterogeneous mixture. | e. | a homogeneous
mixture. | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which
statement concerning NaCl is true? a. | NaCl has properties similar to sodium metal and chlorine
gas. | b. | NaCl is a
homogeneous mixture. | c. | NaCl is a heterogeneous mixture. | d. | The percentage
of Na in NaCl is dependent on where the sample is obtained. | e. | NaCl is composed
of ions, which are electrically charged atoms. | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
The
molecular model depicts a molecule composed of carbon (black), oxygen (gray), and hydrogen (white.
atoms. What is the correct molecular formula?
a. | CHO | b. | C6H6O2 | c. | C6H7O | d. | C7H6O | e. | C7H6O2 | | |
|
|
|
6.
|
All
of the following are examples of physical properties EXCEPT a. | the density of
neon gas. | b. | the conductivity of copper wire. | c. | the boiling
point of water. | d. | the frying of an egg. | e. | the density of
mercury metal. | | |
|
|
|
7.
|
All
of the following are examples of chemical change EXCEPT a. | the condensation
of steam. | b. | the rusting of iron. | c. | the combustion
of propane gas. | d. | the tarnishing of silver. | e. | the
decomposition of water to hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. | | |
|
|
|
8.
|
When
12 copper pennies are submerged in water, the pennies displace 4.13 cm3 of water. If the
combined mass of the pennies is 36.93 g, what is the density of copper? a. | 0.745
g/cm3 | b. | 3.49 g/cm3 | c. | 8.94
g/cm3 | d. | 32.8 g/cm3 | e. | 153
g/cm3 | | |
|
|
|
9.
|
Thermostats are often set to 72°F. What is this temperature in
Celsius? a. | 8°C | b. | 22°C | c. | 37°C | d. | 58°C | e. | 72°C | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which
is a correct method for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius? a. | °C = 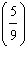 °F + 32 °F + 32 | b. | °C = 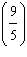 °F + 32 °F + 32 | c. | °C = 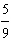 (°F + 32) (°F + 32) | d. | °C = 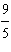 (°F - 32) (°F - 32) | e. | °C = 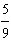 (°F - 32) (°F - 32) | | |
|
|
|
11.
|
The
temperature required to melt NaCl is 801 K. What is this temperature in Celsius? a. | 298°C | b. | 327°C | c. | 528°C | d. | 852°C | e. | 1074°C | | |
|
|
|
12.
|
According to the kinetic-molecular theory of matter, particles in a
liquid a. | are packed
closely together in a regular array. | b. | are close together, but they are not confined to specific
positions. | c. | expand to fill their container. | d. | vibrate back and
forth about an average position. | e. | move slower as the temperature
increases. | | |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which
of the following is a homogeneous mixture? a. | italian salad dressing | b. | chocolate chip
ice cream | c. | gasoline | d. | a rock, such as
granite or marble | e. | a jar of chunky peanut butter | | |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which
term best describes ethylene glycol, C2H6O2? a. | chemical
compound | b. | solution | c. | homogeneous
mixture | d. | heterogeneous mixture | e. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
15.
|
A
common wavelength of light emitted from a red laser pointer is 6.50 ´ 102
nm. What is the wavelength in meters? a. | 6.50 ´ 10-9 m | b. | 6.50
´ 10-7
m | c. | 6.50
´ 10-5
m | d. | 6.50
´ 10-3
m | e. | 6.50
´ 100
m | | |
|
|
|
16.
|
A
rectangular box has dimensions of 20.0 cm ´ 15.0 cm ´ 8.00 cm. Calculate the volume of the box in liters. a. | 2.40
´ 10-3
L | b. | 4.30
´ 10-3
L | c. | 2.40
L | d. | 43.0
L | e. | 2.40
´ 103
L | | |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which
is a correct method of determining the number of liters of gas required to fill an automobile's 15
gallon tank? (1.000 L = 1.057 quarts, 4 quarts = 1 gallon) a. | 15 gallons 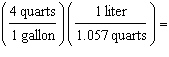 | b. | 15 gallons 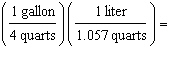 | c. | 15 gallons 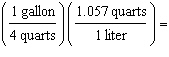 | d. | 15 gallons 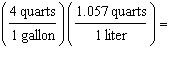 | e. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
18.
|
The
mass of a sample weighed on an electronic balance that is sensitive to ±2 mg is 21.7834 g. What
is the correct number of significant figures for this measurement?
|
|
|
19.
|
Two
electronic balances are tested using a standard weight. The true mass of the standard is 1.0000 g.
The results of 5 individual measurements on each balance are recorded
below.
| | Balance A | Balance
B | | | 0.8888
g | 1.3110 g | | | 0.9959
g | 1.3109 g | | | 1.1182
g | 1.3111 g | | | 1.0033
g | 1.3110 g | | | 0.9938
g | 1.3110 g | average mass = | 1.0000
g | 1.3110 g | | | |
Which statement best describes the
results? a. | A: good
precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, good accuracy | b. | A: good
precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, poor accuracy | c. | A: poor
precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, good accuracy | d. | A: poor
precision, good accuracy. B: good precision, poor accuracy | e. | A: poor
precision, good accuracy. B: poor precision, poor accuracy | | |
|
|
|
20.
|
Express 0.05620 in exponential notation. a. | 5.6 ´
10-2 | b. | 5.62 ´ 10-2 | c. | 5.620
´
10-2 | d. | 5.6 ´ 102 | e. | 5.62
´
102 | | |
|
|
|
21.
|
All
atoms of the same element have the same number of ________ in their nucleus. a. | neutrons | b. | electrons | c. | protons | d. | neutrons and protons | e. | neutrons,
protons, and electrons | | |
|
|
|
22.
|
All
of the following statements are true EXCEPT a. | for any neutral element, the number of protons and electrons
are equal. | b. | isotopes of an element have the same atomic
number. | c. | the mass number is the sum of the number of protons and
neutrons. | d. | the atomic number equals the number of
protons. | e. | all atoms of a given element have the same mass
number. | | |
|
|
|
23.
|
How
many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a carbon-13 atom? a. | 6 protons, 6
neutrons, 1 electron | b. | 6 protons, 7 neutrons, 6 electrons | c. | 7 protons, 6
neutrons, 6 electrons | d. | 7 protons, 6 neutrons, 7 electrons | e. | 13 protons, 13
neutrons, 13 electrons | | |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which
two of the ions below have the same number of electrons?
a. | | b. | | c. | | d. | | e. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which
two of the following atoms are isotopes?
a. | | b. | | c. | | d. | | e. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
26.
|
What
is the identity of 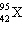 ? ? a. | molybdenum | b. | technetium | c. | americium | d. | copper | e. | iodine | | |
|
|
|
27.
|
What
is a correct method for calculating the mass of 3.0 ´ 1022 sodium atoms? a. | 3.0 ´ 1022
atoms Na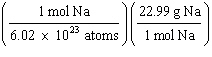 | b. | 3.0 ´ 1022
atoms Na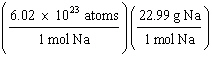 | c. | 3.0 ´ 1022
atoms Na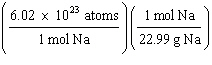 | d. | 3.0 ´ 1022
atoms Na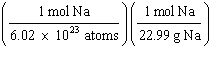 | e. | 6.02
´ 1023
atoms Na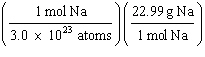 | | |
|
|
|
28.
|
How
many elements are in the second period of the periodic table?
|
|
|
29.
|
What
element is in the third period in Group 5A?
|
|
|
30.
|
Which
three elements are likely to have similar chemical and physical properties? a. | nitrogen,
oxygen, and neon | b. | sodium, magnesium, and aluminum | c. | calcium,
strontium, and barium | d. | nickel, copper, and zinc | e. | uranium,
plutonium, and americium | | |
|
|
|
31.
|
The
smallest unit into which a pure substance such as sugar or water can be divided, while still
retaining its composition and chemical properties is a(n) ________. a. | atom | b. | molecule | c. | isotope | d. | mixture | e. | ion | | |
|
|
|
32.
|
Acetylsalicylic acid, commonly known as aspirin, has 9 carbon atoms, 8 hydrogen atoms,
and 4 oxygen atoms per molecule. What is the molecular formula of aspirin? a. | C9H8O4 | b. | Ca9H8O2 | c. | C9He8O4 | d. | C9H8Ox4 | e. | C9(HO4)2 | | |
|
|
|
33.
|
A
bromide ion has ________ electrons.
|
|
|
34.
|
Identify the ions present in K2HPO4. a. | K+
and HPO42- | b. | K22+, H+, and
PO43- | c. | K+, H+, P3-, and
O2- | d. | K2H3+ and
PO43- | e. | K2HPO4 is not
ionic. | | |
|
|
|
35.
|
Identify the ions in (NH4)2SO4. a. | N3-,
H+, S2-, and O2- | b. | NH22+ and H2SO4 | c. | NH4+ and SO42- | d. | NH42+ and SO42- | e. | NH4+ and SO4- | | |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which
atom is most likely to form a -2 ion?
|
|
|
37.
|
Which
atom is most likely to form a +2 ion?
|
|
|
38.
|
All
of the following formulas are correct EXCEPT a. | Ba(NO3)2 | b. | KClO4 | c. | Na3N | d. | Al2(SO4)3 | e. | Ca2HPO4 | | |
|
|
|
39.
|
For a
nonmetal in Group 6A of the periodic table, the most common monatomic ion will have a charge of
________.
|
|
|
40.
|
Which
formula represents the binary compound formed by strontium ions and phosphate ions? a. | Sr2(PO4)3 | b. | SrPO4 | c. | Sr2P3 | d. | Sr3(PO4)2 | e. | SrP | | |
|
|
|
41.
|
What
is the correct formula for a binary compound that contains magnesium and bromine? a. | MgBr | b. | Mg2Br2 | c. | Mg2Br | d. | MgBr2 | e. | Mg2Br3 | | |
|
|
|
42.
|
What
are the integer values for x and y, respectively, for
Alx(CO3)y? a. | 1 and 2 | b. | 2 and
3 | c. | 1 and
3 | d. | 3 and
1 | e. | 3 and
2 | | |
|
|
|
43.
|
What
is the correct formula for potassium nitrate? a. | KN | b. | K3N | c. | KNO | d. | KNO2 | e. | KNO3 | | |
|
|
|
44.
|
What
is the correct formula for magnesium carbonate? a. | Mg2C | b. | MgCO3 | c. | Mg2CO3 | d. | Mg(CO3)2 | e. | Mg3(CO3)2 | | |
|
|
|
45.
|
What
is the correct formula for aluminum sulfide? a. | AlSO3 | b. | Al2(SO4)3 | c. | AlS | d. | Al3(SO3)2 | e. | Al2S3 | | |
|
|
|
46.
|
What
is the correct name for NH4NO3? a. | ammonium
nitrate | b. | nitrogen tetrahydronitrogen trioxide | c. | nitrogen
tetrahydronitrate | d. | tetrahydronitrogen nitrate | e. | dinitrogen
hydrogenate | | |
|
|
|
47.
|
What
is the correct name for CoBr2? a. | cobalt(II) dibromate | b. | cobalt(II)
dibromide | c. | cobalt bromine | d. | monocobalt
dibromate | e. | cobalt(II) bromide | | |
|
|
|
48.
|
What
is the common name for NH3? a. | mononitrogen trihydrogen | b. | hydrazine | c. | nitrogen | d. | ammonia | e. | trihydrogen nitride | | |
|
|
|
49.
|
What
is the common name for N2O4? a. | nitrogen
tetraoxide | b. | di(nitrogen dioxide) | c. | dinitrogen
oxide | d. | dinitroxide | e. | dinitrogen
tetraoxide | | |
|
|
|
50.
|
The
empirical formula of a hydrocarbon with a molar mass of 78.11 g/mol is CH. What is the molecular
formula? a. | C6H6 | b. | C5H28 | c. | C5H2O | d. | C2H4 | e. | C8H18 | | |
|
|
|
51.
|
What
is the molar mass of nitroglycerine,
C3H5(ONO2)3? a. | 41.07
g/mol | b. | 227.1 g/mol | c. | 103.1
g/mol | d. | 165.1 g/mol | e. | 204
g/mole | | |
|
|
|
52.
|
What
is the mass percent of iron in iron(II) oxalate, FeC2O4? a. | 14.29% | b. | 61.18% | c. | 32.07% | d. | 38.82% | e. | 81.17% | | |
|
|
|
53.
|
A
molecule is found to contain 47.35% C, 10.60% H, and 42.05% O. What is the empirical formula for this
molecule? a. | C2H6O | b. | C2H6O2 | c. | C3H8O2 | d. | C3H6O3 | e. | C4H6O | | |
|
|
|
54.
|
Sulfur dioxide may be prepared by the reaction of sulfur with oxygen gas according to
the chemical equation below.
__
S8(s) + __ O2(g) ® __ SO2(g)
What are the respective coefficients when the equation is balanced
with the smallest whole numbers? a. | 8, 8, 8 | b. | 2, 16,
8 | c. | 1, 8,
8 | d. | 2, 16,
16 | e. | 1, 2,
1 | | |
|
|
|
55.
|
When
ethanol undergoes complete combustion, the products are carbon dioxide and
water.
__ C2H5OH(ª) + __
O2(g) ® __ CO2(g) + __
H2O(g)
What are the respective coefficients when the equation
is balanced with the smallest whole numbers? a. | 2, 7, 4, 6 | b. | 1, 3, 2,
3 | c. | 2, 2, 1,
4 | d. | 1, 2, 3,
2 | e. | 2, 4, 6,
4 | | |
|
|
|
56.
|
The
products of the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon are carbon dioxide and water. Write a balanced
chemical equation for the combustion of butane, C4H10. a. | 2
C4H10(g) + 13 O2(g) ® 8 CO2(g) + 10
H2O(g) | b. | C4H10(g) ® 4 C(s) + 4
H2(g) | c. | C4H10(g) + 13 O2(g)
® 4
CO2(g) + 5 H2O(g) | d. | C4H10(g) + 9 O2(g)
® 4
CO2(g) + 5 H2O(g) | e. | None of the above are correctly
balanced. | | |
|
|
|
57.
|
Aluminum reacts with oxygen to produce aluminum oxide.
4 Al(s) + 3 O2(g) ® 2 Al2O3(s)
If 3.0 moles of Al reacts with excess O2, how many moles of
Al2O3 can be formed? a. | 1.5 mol | b. | 2.0
mol | c. | 2.7
mol | d. | 3.0
mol | e. | 4.5
mol | | |
|
|
|
58.
|
What
mass of carbon is needed to react completely with 23.14 grams of SiO2 according to the
following equation?
SiO2(s) + 3 C(s) ® SiC(s) + 2
CO(g) a. | 1.16
g | b. | 4.62
g | c. | 13.9
g | d. | 38.6
g | e. | 116
g | | |
|
|
|
59.
|
What
is a correct method for determining how many grams of oxygen will react with 1.00 gram of
propane?
C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g)
® 3
CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g)
a. | 1.00g C3H8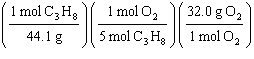 = = | b. | 1.00g C3H8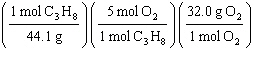 = = | c. | 1.00g C3H8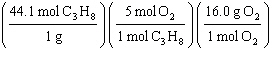 = = | d. | 1.00g C3H8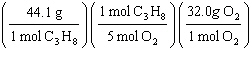 = = | e. | 1.00g C3H8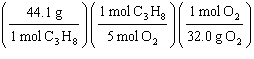 = = | | |
|
|
|
60.
|
What
is a correct method for determining how many moles of magnesium oxide will be formed from the
reaction of 5.00 g magnesium with excess oxygen?
2 Mg(s) + O2(g) ® 2 MgO(s)
a. | 5.00g Mg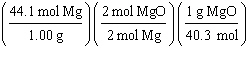 | b. | 5.00g Mg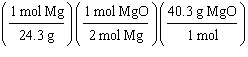 | c. | 5.00g Mg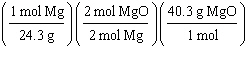 | d. | 5.00g Mg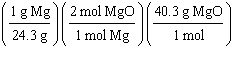 | e. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
61.
|
Which
one of the following solutions will have the highest electrical conductivity? a. | 0.010 M
KCl | b. | 0.010 M
CaI2 | c. | 0.010 M MgSO4 | d. | 0.010 M
Al(NO3)3 | e. | 0.010 M Na2SO4 | | |
|
|
|
62.
|
Which
statement about the reaction below is correct?
K2SO4 + Ba(NO3)2
®
BaSO4 + 2 KNO3 a. | BaSO4 will precipitate. | b. | KNO3
will precipitate. | c. | Both BaSO4 and KNO3 will
precipitate. | d. | Neither BaSO4 nor KNO3 will
precipitate. | e. | No reaction will occur because K2SO4 is
insoluble. | | |
|
|
|
63.
|
Which
of the following compounds is a weak acid? a. | HCl | b. | HF | c. | HBr | d. | HNO3 | e. | HClO4 | | |
|
|
|
64.
|
What
is the net ionic equation for the reaction below?
AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) ® AgBr(s) +
KNO3(aq) a. | K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) ®
KNO3(s) | b. | AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) ®
AgBr(s) | c. | K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) ®
KNO3(aq) | d. | AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) ® AgBr(s) +
KNO3(aq) | e. | Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq) ®
AgBr(s) | | |
|
|
|
65.
|
What
is the net ionic equation for the reaction of sodium hydroxide with iron(III)
nitrate? a. | 3
Na+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) ® Na3Fe(s) | b. | NaOH(aq) +
FeNO3(aq) ® FeOH(s) + NaNO3(aq) | c. | Fe3+(aq) + 3 NO3-(aq) ®
Fe(NO3)3(s) | d. | Fe3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq) ®
Fe(OH)3(s) | e. | Na+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
®
NaNO3(s) | | |
|
|
|
66.
|
What
is the net ionic equation for the reaction of potassium hydroxide and hydrochloric
acid? a. | H+(aq) + KOH(aq) ® H2O(ª) + K+(aq) | b. | K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) ® KCl(aq) | c. | HCl(aq) +
KOH(aq) ®
H2O(ª) | d. | H+(aq) + OH-(aq) ®
H2O(ª) | e. | KOH(aq) + H2O(ª) ®
H+(aq) + K(OH)2(s) | | |
|
|
|
67.
|
What
is the oxidation number of manganese in KMnO4?
|
|
|
68.
|
What
is the oxidation number of phosphorus in CaHPO4?
|
|
|
69.
|
If
1.928 g KNO3 is dissolved in enough water to make 250.0 mL of solution, what is the
molarity of potassium nitrate? a. | 6.912 ´ 10-4 M | b. | 4.767
´ 10-3
M | c. | 7.627
´ 10-2
M | d. | 1.297
´ 10-1
M | e. | 7.712
M | | |
|
|
|
70.
|
Which
of the following directions correctly describe the preparation of 0.500 L of 0.150 M NaOH from a 6.00
M stock solution? a. | Dilute 0.200 L
of 6.00 M NaOH to a volume of 0.500 L. | b. | Dilute 12.5 mL of 6.00 M NaOH to a volume of 0.500
L. | c. | Combine 0.200 L
of 6.00 M NaOH with 0.500 L of water. | d. | Dilute 475 mL of 6.00 M NaOH to a volume of 0.500
L. | e. | Combine 12.5 mL
of 6.00 M NaOH with 0.500 L of water. | | |
|
|
|
71.
|
Potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) is a weak acid that is used to standardize sodium
hydroxide according to the net ionic equation below.
HC8H4O4-(aq) +
OH-(aq) ® H2O(ª) +
C8H4O42-(aq)
If 1.02 g KHP (molar mass = 204.2 g/mol) is titrated with 28.34 mL of
NaOH, what is the concentration of NaOH? a. | 0.03536 M | b. | 0.1385
M | c. | 0.2004
M | d. | 0.2176
M | e. | 0.2713
M | | |
|
|
|
72.
|
All
of the following statements are true EXCEPT a. | In an endothermic process heat is transferred from the
surroundings to the system. | b. | The greater the specific heat of an object, the more thermal
energy it can store. | c. | The SI unit of specific heat capacity is joules per gram per
kelvin. | d. | Heat is transferred from the system to the surroundings in an
exothermic process. | e. | The temperature of a system is a state
function. | | |
|
|
|
73.
|
Specific heat capacity is a. | the quantity of heat required to melt 1.00 g of a
substance. | b. | the mass of a substance 1.00 J of energy will heat by 1.00
K. | c. | the mass of a
substance 1.00 cal of energy will heat by 1.00 K. | d. | the temperature
change undergone when 1.00 g of a substance absorbs 1.00 cal. | e. | the quantity of
heat needed to change 1.00 g of a substance by 1.00 K. | | |
|
|
|
74.
|
If
34.8 J is required to change the temperature of 10.0 g of mercury by 25 K, what is the specific heat
of mercury? a. | 0.139
J/g·K | b. | 0.338 J/g·K | c. | 0.718
J/g·K | d. | 0.870 J/g·K | e. | 1.93
J/g·K | | |
|
|
|
75.
|
Calculate the amount of heat required to change 35.0 g ice at -25.0ºC to steam at 125ºC. (Heat of
fusion = 333 J/g; heat of vaporization = 2260 J/g; specific heats: ice = 2.09 J/g·K, water =
4.18 J/g·K, steam = 1.84 J/g·K) a. | 22.0 kJ | b. | 90.9
kJ | c. | 109
kJ | d. | 276
kJ | e. | 3290
kJ | | |
|
|
|
76.
|
10.0
g of ice at 0.00ºC is mixed with 50.0 g of water at 32.0ºC. What is the final temperature of the mixture? (Heat of fusion = 333
J/g; specific heats: ice = 2.09 J/g·K, water = 4.184 J/g·K) a. | -4.59ºC | b. | 0.00ºC | c. | 4.59ºC | d. | 13.4ºC | e. | 23.8ºC | | |
|
|
|
77.
|
Calculate DE of a gas for a process in which the gas absorbs 42 J of heat and does 14 J of
work on the surroundings (i.e. the gas expands)? a. | -56 J | b. | -28
J | c. | +28
J | d. | +42
J | e. | +56
J | | |
|
|
|
78.
|
For a
particular process q = 25 kJ and w = -15 kJ. What conclusions may be drawn for this
process? a. | DE = 40
kJ | b. | DE = -40
kJ | c. | This is a
product favored reaction. | d. | Work is done by the system on the
surroundings. | e. | Both answer b and d are correct. | | |
|
|
|
79.
|
One
statement of the first law of thermodynamics is that a. | the amount of
work done on a system is independent of pathway. | b. | the total energy
flow in or out of a system is equal to the sum of the heat absorbed and the work done on the
system. | c. | the heat flow in or out of a system is independent of
pathway. | d. | the total work done on a system must equal the heat absorbed by
the system. | e. | in any chemical process the sum of the heat flow and the work
must equal zero. | | |
|
|
|
80.
|
Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of carbon
monoxide,
C(s) + 1/2 O2(g) ® CO(g), given
the enthalpies of the reactions below.
C(s) +
O2(g) ® CO2(g) | DH =
-393.5 kJ | 2 CO(g) + O2(g) ® 2
CO2(g) | DH = -566.0 kJ | | |
a. | -959.6
kJ | b. | -421.6
kJºC | c. | -172.5 kJ | d. | -110.5
kJ | e. | 172.5
kJ | | |
|
|
|
81.
|
Calculate the enthalpy for the formation of calcium carbonate from calcium oxide and
carbon dioxide,
CaO(s) + CO2(g) ®
CaCO3(s)
given the enthalpies of the reactions
below.
2 Ca(s) +
O2(g) ® 2 CaO(s) | DH = -1270.2 kJ | C(s) + O2(g) ® CO2(g) | DH =
-393.5 kJ | 2 Ca(s) + 2 C(s) + 3 O2(g) ® 2
CaCO3(s) | DH = -2413.8 kJ | | |
a. | -4077.3
kJ | b. | -2235.5
kJ | c. | -750.1
kJ | d. | -350.2
kJ | e. | -178.3
kJ | | |
|
|
|
82.
|
Determine the heat of reaction for the oxidation of iron,
4 Fe(s) + 3 O2(g) ® 2 Fe2O3(s)
given the enthalpies of the reactions
below.
2 Fe(s) + 6
H2O(ª) ® 2 Fe(OH)3(s) + 3
H2(g) | DH = 321.8 kJ | 2
H2(g) + O2(g) ® 2 H2O(ª) | DH = -571.7 kJ | Fe2O3(s) + 3 H2O(ª) ® 2
Fe(OH)3(s) | DH = 288.6 kJ | | |
a. | -1648.7
kJ | b. | -636.9
kJ | c. | -505.3
kJ | d. | 387.0
kJ | e. | +1447.1
kJ | | |
|
|
|
83.
|
Calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion of
C3H6(g),
C3H6(g) + 9/2 O2(g) ® 3
CO2(g) + 3 H2O(ª)
using standard
enthalpies of formation.
molecule | DHfº (kJ) | C3H6(g) | +53.3 | CO2(g) | -393.5 | H2O(ª) | -285.8 | | |
a. | -2091.2
kJ | b. | -1984.6
kJ | c. | -187.8
kJ | d. | -62.6
kJ | e. | +732.3
kJ | | |
|
|
|
84.
|
What
type of orbital is designated n = 4, ª = 2, mª = +1?
|
|
|
85.
|
What
type of orbital is designated n = 2, ª = 0, mª = 0?
|
|
|
86.
|
All
of the following sets of quantum numbers are allowed EXCEPT a. | n =
6,ª = 4,
mª = +2 | b. | n = 3,
ª = 2,
mª = -1 | c. | n = 4,
ª = 1,
mª = 0 | d. | n = 1,
ª = 0,
mª = 0 | e. | n = 2,
ª = 3,
mª = +3 | | |
|
|
|
87.
|
What
is the maximum number of orbitals when n = 6 and ª = 2?
|
|
|
88.
|
The
n = _____ shell is the lowest that may contain an f-orbital.
|
|
|
89.
|
Which
of the following diagrams represents a d-orbital?
a. | (I)
only | b. | (II)
only | c. | (III)
only | d. | (IV)
only | e. | (I) and
(IV) | | |
|
|
|
90.
|
Which
of the following diagrams represent a p-orbital?
a. | (I)
only | b. | (II)
only | c. | (III)
only | d. | (IV)
only | e. | (I) and
(II) | | |
|
|
|
91.
|
The
Pauli exclusion principle states that a. | electrons can have either positive or negative _
spins. | b. | no two electrons in an atom can have the same 4 quantum
numbers. | c. | two electrons can share the same orbital if they have the same
spin. | d. | no two electrons in an atom can have the same
spin. | e. | atoms with one or more unpaired electrons are
paramagnetic. | | |
|
|
|
92.
|
What
is the maximum number of electrons that can exist in the shell n = 2?
|
|
|
93.
|
Which
+3 ion has the electron configuration [Ar]3d3?
|
|
|
94.
|
If
the electron configuration of an element is
[Ar]3d104s24p4, what is the charge on the
monoatomic anion of the element?
|
|
|
95.
|
What
is the electron configuration for Cu+? a. | [Ar] | b. | [Ar]3d8 | c. | [Ar]4s23d8 | d. | [Ar]3d10 | e. | [Ar]4s13d9 | | |
|
|
|
96.
|
What
is the electron configuration for an iodine atom? a. | [Kr]4d105s25p5 | b. | [Kr]4f145d106s26p5 | c. | [Kr]5d106s26p5 | d. | [Xe]5p-1 | e. | [Kr]4d104f145d5 | | |
|
|
|
97.
|
Which
of the following atoms and ions have the same electron configuration: I-, Pb4+,
Xe, Ba2+ and Sn2+? a. | I-, Xe, and
Ba2+ | b. | I-, Pb4+, Xe, and
Ba2+ | c. | Pb4+ and Sn2+ | d. | Pb4+
and Ba2+ | e. | none of the above | | |
|
|
|
98.
|
What
element has the following electron configuration?
|
|
|
99.
|
What
-1 ion the following electron configuration?
|
|
|
100.
|
Which
type of elements have no affinity for electrons? a. | transition metals | b. | main group
metals | c. | noble gases | d. | main group
nonmetals | e. | semiconductors | | |
|
|
|
101.
|
Which
group of the periodic table elements forms only +1 ions? a. | group
1A | b. | group
2A | c. | group
7B | d. | group
7A | e. | group
8A | | |
|
|
|
102.
|
Which
of the following ions is least likely to be formed? a. | Al3+ | b. | Cu+ | c. | Na+ | d. | Ti4+ | e. | Sr3+ | | |
|
|
|
103.
|
What
is the expected number of valence electrons for a group 3A element?
|
|
|
104.
|
Which
of the following elements is most likely to form a molecule that exceeds the octet
rule?
|
|
|
105.
|
Which
of the following combinations is most likely to produce ionic bonds? a. | O and
H | b. | Al and
S | c. | C and
N | d. | N and
O | e. | S and
Cl | | |
|
|
|
106.
|
When
both of the electrons in a molecular bond originate from the same atom, the bond is called
a(n) a. | ionic
bond. | b. | free radical bond. | c. | coordinate
covalent bond. | d. | Lewis dot structure. | e. | double
bond. | | |
|
|
|
107.
|
What
is the total number of valence electrons in a carbon tetrachloride molecule?
|
|
|
108.
|
Which
of the following is a correct Lewis structure for SO2?
|
|
|
109.
|
H3PO3 is a diprotic acid (i.e. it has two acid functions). Which
of the following Lewis structures is most likely correct for
H3PO3?
|
|
|
110.
|
Which
of the following is a correct Lewis structure for sulfate ion?
|
|
|
111.
|
Which
of the following is a possible Lewis structures for
C2H6O?
a. | 1 | b. | 2 | c. | 3 | d. | 1 and 2 | e. | 1 and
3 | | |
|
|
|
112.
|
Electronegativity is a measure of a. | the charge on an electron. | b. | a molecule's
polarity. | c. | the charge on an atom. | d. | the number of
extra electrons on an anion. | e. | an atom's ability to attract electrons to
itself. | | |
|
|
|
113.
|
Predict which of the following compounds will have the bond that is most
polar.
|
|
|
114.
|
When
heated, azomethane decomposes into nitrogen gas and methane gas.
CH3N=NCH3(g) ®
N2(g) + C2H6(g)
Bond | Bond Enthalpy (kJ/mol) | |
Bond | Bond Enthalpy
(kJ/mol) | C-H | 413 | | N-N | 163 | C-N | 305 | | N=N | 418 | C-C | 346 | | NºN | 945 | | | | | |
Using average
bond enthalpies, calculate the enthalpy of reaction. a. | -609
kJ/mol | b. | -583 kJ/mol | c. | -462
kJ/mol | d. | -263 kJ/mol | e. | -197
kJ/mol | | |
|
|
|
115.
|
Use
VSEPR theory to predict the electron pair geometry and the molecular geometry of
SO2. a. | e-
pair geometry = trigonal planar, molecular geometry = bent | b. | e-
pair geometry = trigonal planar, molecular geometry = linear | c. | e-
pair geometry = tetrahedral, molecular geometry = bent | d. | e-
pair geometry = tetrahedral, molecular geometry = trigonal planar | e. | e-
pair geometry = tetrahedral, molecular geometry = linear | | |
|
|
|
116.
|
Use
VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry of SF2. a. | bent | b. | linear | c. | trigonal
pyramidal | d. | tetrahedral | e. | octahedral | | |
|
|
|
117.
|
Use
VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry HCN. a. | bent | b. | linear | c. | trigonal
planar | d. | tetrahedral | e. | octahedral | | |
|
|
|
118.
|
Use
VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry of BCl3. a. | bent | b. | trigonal pyramidal | c. | trigonal
planar | d. | tetrahedral | e. | t-shaped | | |
|
|
|
119.
|
What
are the bond angles in SCN-? a. | 90° | b. | 109° | c. | 120° | d. | 180° | e. | 90° and 109° | | |
|
|
|
120.
|
What
are the bond angles in SiH4? a. | 90° | b. | 109° | c. | 120° | d. | 180° | e. | 90° and 109° | | |
|
|
|
121.
|
How
many sigma (s) bonds and pi
(p) bonds are in
the following molecule?
a. | seven
s and two
p | b. | six s and two p | c. | eleven s and zero p | d. | nine s and two p | e. | two s and nine p | | |
|
|
|
122.
|
How
many sigma (s) bonds and pi
(p) bonds are in acetone?
a. | eight
s and one
p | b. | six s and one p | c. | nine s and one p | d. | one s and nine p | e. | one s and eight p | | |
|
|
|
123.
|
In
order to form a set of sp hybrid orbitals, how many pure atomic orbitals must be
mixed? a. | one s,
one p | b. | two s, one p | c. | two s,
two p | d. | one s, two p | e. | zero s,
two p | | |
|
|
|
124.
|
In
order to form a set of sp3d hybrid orbitals, how many pure atomic orbitals
must be mixed? a. | one s,
one p, and one d | b. | one s, three p, and one
d | c. | two s, one p, and two
d | d. | two s, six p, and two
d | e. | none of the above | | |
|
|
|
125.
|
What
is the maximum number of hybridized orbitals that can be formed by a nitrogen atom?
|
|
|
126.
|
What
is the maximum number of hybridized orbitals that can be formed by xenon?
|
|
|
127.
|
In
which of the following molecules does the carbon atom have sp hybridization: HCN,
CH4, CO2, and CH2O? a. | CH4
only | b. | CH4
and CH2O | c. | HCN and CH2O | d. | HCN and
CO2 | e. | HCN, CO2, and
CH2O | | |
|
|
|
128.
|
In
which of the following molecules or ions does the central atom have sp2
hybridization: NH2-, H2O, BH3,
SO2? a. | NH2- and BH3 | b. | H2O
and SO2 | c. | H2O, BH3, and
SO2 | d. | NH2-, H2O, and
SO2 | e. | BH3 and SO2 | | |
|
|
|
129.
|
What
is the hybridization of each oxygen atom in O2? a. | sp | b. | sp2 | c. | sp3 | d. | sp3d | e. | sp3d2 | | |
|
|
|
130.
|
What
is the hybridization of the sulfur atom in sulfate ion, SO42-? a. | sp | b. | sp2 | c. | sp3 | d. | sp3d | e. | sp3d2 | | |
|
|
|
131.
|
What
is the molecular geometry around an atom that is sp3 hybridized and has two lone
pairs of electrons? a. | bent | b. | linear | c. | trigonal
pyramidal | d. | trigonal planar | e. | trigonal
bipyramidal | | |
|
|
|
132.
|
What
is the molecular geometry around an atom that is sp3 hybridized, has three sigma
bonds, no pi bonds, and one lone pair? a. | bent | b. | linear | c. | trigonal
pyramidal | d. | trigonal planar | e. | tetrahedral | | |
|
|
|
133.
|
What
is the molecular geometry around an atom that is sp hybridized, has two sigma bonds, two pi
bonds, and no lone pairs? a. | bent | b. | linear | c. | trigonal
planar | d. | tetrahedral | e. | octahedral | | |
|
|
|
134.
|
Which
of the following hybridized atoms is not possible? a. | an sp
hybridized oxygen atom | b. | an sp3 hybridized nitrogen
atom | c. | an
sp2 hybridized carbon atom | d. | an
sp2 hybridized boron atom | e. | an
sp3d2 hybridized fluorine atom | | |
|
|
|
135.
|
At
constant temperature, 10.0 L of N2 at 0.983 atm is compressed to 2.88 L. What is the final
pressure of N2? a. | 0.283 atm | b. | 0.293
atm | c. | 2.98
atm | d. | 3.41
atm | e. | 28.3
atm | | |
|
|
|
136.
|
Avogadro's law states that equal volumes of gases under the same conditions of
temperature and pressure have equal ________. a. | masses | b. | numbers of
molecules | c. | molar masses | d. | densities | e. | velocities | | |
|
|
|
137.
|
Which
of the following relationships are true for gases?
1. The volume of a gas is directly proportional to its pressure in mm
Hg.
2. The pressure of a gas in inversely proportional to its temperature in
kelvin.
3. The moles of a gas are directly proportional to the gas constant
R. a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 2 and
3 | e. | none are
true | | |
|
|
|
138.
|
Ammonia gas is synthesized according to the balanced equation
below.
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ® 2
NH3(g)
If 2.50 L N2 react with 7.00 L
H2, what is the theoretical yield (in liters) of NH3? Assume that the volumes
of reactants and products are measured at the same temperature and pressure. a. | 2.50
L | b. | 4.67
L | c. | 5.00
L | d. | 7.00
L | e. | 10.5
L | | |
|
|
|
139.
|
Which
of the following are postulates of kinetic-molecular theory of gases?
1. The distance between gas molecules is large in comparison to their
size.
2. The velocity of a gas molecule is inversely proportional to its
temperature.
3. Gas molecules are in constant, random
motion.
4. At a given temperature, all gases have the same average kinetic
energy.
a. | 1 and
4 | b. | 1, 2, and
4 | c. | 1, 3, and
4 | d. | 2 and
3 | e. | 3 and
4 | | |
|
|
|
140.
|
Non-ideal behavior for a gas is most likely to be observed under conditions
of a. | high temperature
and high pressure. | b. | low temperature and high pressure. | c. | low temperature
and low pressure. | d. | standard temperature and pressure. | e. | high temperature
and low pressure. | | |
|
|
|
141.
|
One
way in which real gases differ from ideal gases is that the molecules of a real gas a. | have no kinetic
energy. | b. | occupy no volume. | c. | are attracted to
each other. | d. | have positive and negative spins. | e. | are always
polar. | | |
|