Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Ideally, collligative properties depend only on a. | the identity of
the solute in a solution. | b. | the number of solute particles per solvent molecule in a
solution. | c. | the temperature of a solution. | d. | the charge of
the ions dissolved in solution. | e. | the gas pressure above the surface of a
solution. | | |
|
|
|
2.
|
What
is the definition of molality? a. | moles of solute per liter of solution | b. | grams of solute
per kg of solution | c. | grams of solute per kg of solvent | d. | moles of solute
per kg of solvent | e. | moles of solute per liter of solvent | | |
|
|
|
3.
|
To
prepare approximately 1 liter of a solution that is 4.75% by mass NaCl, one should a. | dissolve 4.75 g
NaCl in water up to a total volume of 1.00 L. | b. | dissolve 47.5 g
NaCl in 1.00 ´ 103 g water. | c. | dissolve 47.5 g
NaCl in 952.5 g water. | d. | dissolve 952.5 g NaCl in 47.5 g
water. | e. | dissolve 46.5 g NaCl in 1.00 kg
water. | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
The
molality of a sodium nitrate solution is 1.44 m. What is the mole fraction of
NaNO3? The molar mass of NaNO3 is 85.06 g/mol; the molar mass of water is 18.02
g/mol. a. | 0.0253 | b. | 0.0571 | c. | 0.122 | d. | 0.688 | e. | 2.21 | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
Concentrated hydrofluoric acid is 49.0% HF by mass and has a density of 1.30 g/mL.
What is the molarity of concentrated HF? a. | 12.1 M | b. | 17.4
M | c. | 18.8
M | d. | 24.5
M | e. | 31.8
M | | |
|
|
|
6.
|
Equal
masses of water and ethylene glycol are mixed. What is the concentration of ethylene glycol in units
of molality? The molar mass of water and ethylene glycol are 18.02 g/mol and 62.07 g/mol,
respectively. a. | 3.21
m | b. | 6.92 m | c. | 11.1
m | d. | 16.1 m | e. | 18.2
m | | |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which
of the following liquids are likely to be miscible with water: 1-propanol, carbon tetrachloride,
cyclohexane, and formic acid (HCO2H)? a. | 1- propanol and cyclohexane | b. | carbon
tetrachloride and cyclohexane | c. | cyclohexane and formic acid | d. | carbon
tetrachloride and formic acid | e. | 1-propanol and formic acid | | |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which
of the following actions will increase the equilibrium concentration of a gas in
water?
1. increasing the temperature of the
water
2. increasing the volume water
3. increasing
the pressure of the gas above the liquid a. | 1 only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
3 | e. | 1, 2, and
3 | | |
|
|
|
9.
|
The
vapor pressure of pure water at 35ºC is 42.2 mm Hg. What is the vapor pressure of a mixture of
15 g sucrose (C12H22O11, molar mass 342.3 g/mol) and 85 g
water? a. | 7.45 mm
Hg | b. | 21.8 mm
Hg | c. | 35.9 mm
Hg | d. | 40.6 mm
Hg | e. | 41.8 mm
Hg | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which
of the following aqueous solutions should have the lowest boiling point? a. | 0.4 m
MgBr2 | b. | 0.5 m
Na2SO4 | c. | 0.75 m NaCl | d. | 1 m
KI | e. | 2 m
LiBr | | |
|
|
|
11.
|
If
1.928 g KNO3 is dissolved in enough water to make 250.0 mL of solution, what is the
molarity of potassium nitrate? a. | 6.912 ´ 10-4 M | b. | 4.767
´ 10-3
M | c. | 7.627
´ 10-2
M | d. | 1.297
´ 10-1
M | e. | 7.712
M | | |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which
of the following directions correctly describe the preparation of 0.500 L of 0.150 M NaOH from a 6.00
M stock solution? a. | Dilute 0.200 L
of 6.00 M NaOH to a volume of 0.500 L. | b. | Dilute 12.5 mL of 6.00 M NaOH to a volume of 0.500
L. | c. | Combine 0.200 L
of 6.00 M NaOH with 0.500 L of water. | d. | Dilute 475 mL of 6.00 M NaOH to a volume of 0.500
L. | e. | Combine 12.5 mL
of 6.00 M NaOH with 0.500 L of water. | | |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which
of the following properties of water can be attributed to hydrogen
bonding?
1. high melting point
2. high heat of
vaporization
3. low vapor pressure
4. high surface
tension a. | 1 and
3 | b. | 2 and
3 | c. | 2, 3, and
4 | d. | 1, 3, and
4 | e. | 1, 2, 3, and
4 | | |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which
of the following processes is exothermic? a. | solid to gas | b. | liquid to
gas | c. | liquid to
solid | d. | solid to liquid | e. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which
process requires the greatest exothermic change in enthalpy for water? a. | vaporization | b. | condensation | c. | sublimation | d. | melting | e. | fusion | | |
|
|
|
16.
|
The
normal boiling point is defined as a. | the pressure of a gas when its temperature reaches 373.15
K. | b. | the temperature
at which the vapor pressure of a substance equals 1 atm. | c. | the temperature
at which water boils. | d. | the pressure at which a liquid boils at 273.15
K. | e. | the sum of the
enthalpies of vaporization and fusion at 298 K. | | |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which
of the following statements are correct?
1. A liquid boils when its vapor pressure is equal to the pressure
above its surface.
2. Above the critical pressure, only the solid phase of a pure
substance can exist.
3. The gas, liquid, and solid phases can all coexist at the critical
point. a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 1 and
3 | | |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which
of the following gases can be liquefied at 25ºC?
Gas | boiling
pt. | critical temp. | N2 | -196ºC | -147ºC | Cl2 | -34ºC | 144ºC | O2 | -183ºC | -119ºC | | | | | |
a. | N2
only | b. | Cl2
only | c. | O2
only | d. | Cl2
and O2 | e. | N2 and O2 | | |
|
|
|
19.
|
In
the unit cell below, element X is within the cell and element Y is at the corners. What is the
formula for this compound?
|
|
|
20.
|
Which
of the following statements concerning the phase diagram below are
correct?
1. Moving from point A to B results in a phase
transition from solid to liquid.
2. Point D lies at the critical
point.
3. At point C, liquid and gas phases coexist at
equilibrium. a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
3 | e. | 2 and
3 | | |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which
of the statements concerning relative rates of reaction is correct for the decomposition of
dinitrogen pentaoxide?
2
N2O5(g) ® 4 NO2(g) + O2(g)
a. | The rate of
disappearance of N2O5 is 1/2 the rate of appearance of
O2. | b. | The rate of appearance of NO2 is 1/4 the rate of
appearance of O2. | c. | The rate of disappearance of N2O5 is 1/2
the rate of appearance of NO2. | d. | The rate of appearance of NO2 equals the rate of
appearance of O2. | e. | The rate of disappearance of N2O5 equals
the rate of appearance of NO2. | | |
|
|
|
22.
|
Given
the initial rate data for the reaction A + B ® C, determine the rate expression for the
reaction.
[A], M | [B],
M | D[C]/Dt (initial) M/s | 0.25 | 0.15 | 1.23
´
10-3 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 3.42
´
10-3 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 2.46
´
10-3 | | | |
a. | 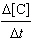 =
0.0328[A][B] =
0.0328[A][B] | b. | 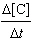 =
0.0547[A][B] =
0.0547[A][B] | c. | 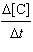 =
0.219[A][B]2 =
0.219[A][B]2 | d. | 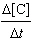 =
0.0547[A][B]2 =
0.0547[A][B]2 | e. | 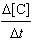 =
0.219[A]2[B] =
0.219[A]2[B] | | |
|
|
|
23.
|
Given
the initial rate data for the reaction A + B ® C, determine the rate expression for the
reaction.
[A], M | [B],
M | D[C]/Dt
(initial) M/s | 0.125 | 0.105 | 1.23
´
10-1 | 0.125 | 0.315 | 3.69
´
10-1 | 0.250 | 0.105 | 1.23
´
10-1 | | | |
a. | 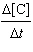 =
75.0[A]2[B] =
75.0[A]2[B] | b. | 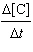 =
1.17[B] =
1.17[B] | c. | 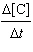 =
1.17[A]2[B] =
1.17[A]2[B] | d. | 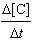 =
11.2[B]2 =
11.2[B]2 | e. | 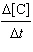 =
11.2[A] =
11.2[A] | | |
|
|
|
24.
|
What
is the overall order of the reaction
CO(g) +
NO2(g) ® CO2(g) + NO(g)
if it proceeds via the following rate
expression?
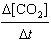 =
k[CO][NO2] =
k[CO][NO2]
a. | zero-order | b. | first-order | c. | second-order | d. | third-order | e. | fourth-order | | |
|
|
|
25.
|
For
the reaction A ® B, the rate law is
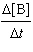 =
k[A] =
k[A]
What are the units of the rate constant where time is
measured in seconds?
|
|
|
26.
|
Which
of the following factors often affect the value of the rate constant of a chemical
reaction?
1. changes in the concentrations of
reactants
2. changes in the temperature of the system
3. the addition
of a catalyst a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 2 and
3 | e. | 1, 2, and
3 | | |
|
|
|
27.
|
The
reaction of NO(g) and O2(g) produces NO2(g).
2 NO(g) + O2(g) ® 2 NO2(g)
The reaction is second-order with respect to NO(g) and first-order
with respect to O2(g). At a given temperature, the rate constant, k, equals 5.7
´ 103
M-2s-1. What is the rate of reaction when the initial concentrations of NO and
O2 are both 0.020 M? a. | 1.4 ´ 10-9 M/s | b. | 4.6 ´ 10-2
M/s | c. | 9.1 ´ 10-2
M/s | d. | 2.3 ´ 100
M/s | e. | 7.1 ´ 108
M/s | | |
|
|
|
28.
|
What
determines the exponents in a rate law?
1. experimentation
2. the
coefficients in the balanced equation
3. the
concentrations of the reactants
a. | 1 only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 2 and
3 | | |
|
|
|
29.
|
The
half-life of a first-order decomposition reaction is 188 seconds. If the initial concentration of
reactant is 0.524 M, what is the concentration of reactant after 752 seconds? a. | 0.0164
M | b. | 0.0328
M | c. | 0.0665
M | d. | 0.133
M | e. | 0.266
M | | |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which
of the following changes generally lead to greater reaction rates?
1. Increasing the temperature
2. Decreasing
the concentration of a reactant
3. Adding a catalyst
a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 1 and
3 | d. | 2 and
3 | e. | 1,2, and
3 | | |
|
|
|
31.
|
In
general, as the temperature increases, the rate of a chemical reaction a. | decreases due to
fewer collisions with proper molecular orientation. | b. | decreases for
endothermic reactions. | c. | decreases for exothermic reactions. | d. | increases due a
greater number of effective collisions. | e. | increases due to a lowering of activation
energy. | | |
|
|
|
32.
|
The
effect of a catalyst is to a. | lower the activation energy of a
reaction. | b. | increase the energy of the products. | c. | increase the
energy of the reactants. | d. | increase the number of collisions between
reactants. | e. | decrease the change in enthalpy of a
reaction. | | |
|
|
|
33.
|
The
elementary steps for the catalyzed decomposition of dinitrogen monoxide are shown below. Identify the
catalyst in the reaction.
N2O(g) + NO(g) ® N2(g) + NO2(g)
2
NO2(g) ® 2 NO(g) + O2(g)
|
|
|
34.
|
In
basic solution, (CH3)3CCl reacts according to the equation
below.
(CH3)3CCl + OH-
®
(CH3)3COH + Cl-
The accepted mechanism for the reaction
is
(CH3)3CCl ® (CH3)3C+ +
Cl- | (slow) | (CH3)3C+ + OH- ®
(CH3)3COH | (fast) | | |
What is the rate law for the
reaction? a. | rate =
k[(CH3)3CCl] | b. | rate =
k[(CH3)3CCl]2 | c. | rate =
k[(CH3)3C+][OH-] | d. | rate =
k[(CH3)3CCl][OH] | e. | rate =
k[(CH3)3CCl][Cl-][OH-] | | |
|
|
|
35.
|
Nitrogen monoxide reacts with chlorine to produce NOCl.
2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) ® 2 NOCl(g)
A proposed mechanism for this reaction is
NO(g) + NO(g)
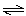 N2O2(g) N2O2(g) | (fast, equilibrium) | N2O2(g) + Cl2(g) ® 2
NOCl(g) | (slow) | | |
What is a rate
law that is consistent with this mechanism? a. | rate = k[NO][Cl2] | b. | rate =
k[[NO]2 | c. | rate =
k[N2O2][Cl2] | d. | rate =
k[NO][Cl2]2 | e. | rate =
k[NO]2[Cl2] | | |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which
of the following statements concerning equilibrium constants are true?
1. Kinetically fast reactions always have large equilibrium
constants.
2. Temperature has no effect on an equilibrium
constant.
3. Reactant favored reactions have negative equilibrium
constants.
a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | none of
above | | |
|
|
|
37.
|
A
large equilibrium constant a. | is obtained with catalysts. | b. | indicates the
formation of products is favored. | c. | is common for equilibria at high
temperatures. | d. | indicates that a reaction has a small activation
barrier. | e. | indicates that a reaction has a large rate
constant. | | |
|
|
|
38.
|
Write
the expression for Kc for the reaction below.
Mg3(PO4)2(s) 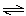 3 Mg2+(aq) + 2
PO43-(aq) 3 Mg2+(aq) + 2
PO43-(aq)
|
|
|
39.
|
Write
the expression for K for the acid reaction below.
HF(aq) + H2O(ª) 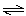 F-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
F-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
|
|
|
40.
|
A
gaseous mixture of NO2 and N2O4 is in equilibrium. If the
concentration of N2O4 is 3.5 ´ 10-3 M, what is the concentration of
NO2?
2 NO2(g) 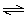 N2O4(g) Kc =
170 N2O4(g) Kc =
170
a. | 2.1 ´ 10-5
M | b. | 4.5 ´ 10-3
M | c. | 7.1 ´ 10-2
M | d. | 2.2 ´ 102
M | e. | 4.9 ´ 104
M | | |
|
|
|
41.
|
We
place 0.064 mol N2O4(g) in a 4.00 L flask at 200. After reaching equilibrium,
the concentration of NO2(g) is 0.0030 M. What is Kc for the reaction
below?
N2O4(g) 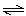 2 NO2(g) 2 NO2(g)
a. | 3.6 ´
10-5 | b. | 4.7 ´ 10-5 | c. | 5.6 ´
10-4 | d. | 6.2 ´ 10-4 | e. | 1.9 ´
10-1 | | |
|
|
|
42.
|
We
place 3.2 mol PCl5 in a 2.0 L flask and allow it to reach equilibrium at a given
temperature. What is the final concentration of Cl2 in the
flask?
PCl5(g) 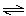 PCl3(aq) +
Cl2(g) Kc =
0.47 PCl3(aq) +
Cl2(g) Kc =
0.47 a. | 0.11
M | b. | 0.27
M | c. | 0.32
M | d. | 0.55
M | e. | 0.66
M | | |
|
|
|
43.
|
Consider the reaction A(g)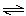 2 B(g) where
Kp = 4.0. If 2.0 mol A and 3.0 mol B are introduced into a 1.0 L flask, what change
in concentrations (if any) will occur in time? 2 B(g) where
Kp = 4.0. If 2.0 mol A and 3.0 mol B are introduced into a 1.0 L flask, what change
in concentrations (if any) will occur in time? a. | [A] increases and [B] increases | b. | [A] increases
and [B] decreases | c. | [A] decreases and [B] increases | d. | [A] decreases
and [B] decreases | e. | [A] and [B] remain unchanged | | |
|
|
|
44.
|
Assume that the following endothermic chemical reaction is at
equilibrium.
C(s) + H2O(g) 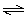 H2(g) + CO(g) H2(g) + CO(g)
All of the
following will increase the ratio of products to reactants in the equilibrium mixture
EXCEPT a. | increasing the
temperature. | b. | increasing the volume. | c. | decreasing the
pressure | d. | addition of solid carbon. | e. | removal of a
gaseous product. | | |
|
|
|
45.
|
The
formation of ammonia from elemental nitrogen and hydrogen is an exothermic
process.
N2(g)
+ 3 H2(g) 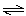 2 NH3(g) 2 NH3(g)
| H = -92.2 kJ | | |
Which of the
following would drive the equilibrium system to the left? a. | addition of
hydrogen | b. | removal of ammonia | c. | increasing the
pressure | d. | decreasing the temperature | e. | removal of
nitrogen | | |
|
|
|
46.
|
In
which of the following equilibrium systems would a decrease in volume have no effect on the
concentrations of products and reactants? a. | CaCO3(s)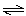 CaO(s) +
CO2(g) CaO(s) +
CO2(g) | b. | N2(g) + 3 H2(g)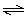 2 NH3(g) 2 NH3(g) | c. | H2(g)
+ CO2(g)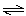 CO(g) + H2O(g) CO(g) + H2O(g) | d. | 3
O2(g)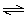 2 O3(g) 2 O3(g) | e. | 2
H2O2(g)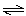 2
H2O(g) + O2(g) 2
H2O(g) + O2(g) | | |
|
|
|
47.
|
According to the Brønsted-Lowry definition, a base a. | increases the
H3O+ concentration in a solution. | b. | increases the
OH- concentration in a solution. | c. | is a proton
donor. | d. | is a proton acceptor. | e. | has a lone pair
of electrons that can bond to a proton. | | |
|
|
|
48.
|
All
of the following are weak acids EXCEPT a. | HF | b. | CH3CO2H | c. | HBr | d. | NH4+ | e. | HCN | | |
|
|
|
49.
|
In
the following reaction
HCO3-(aq) + NH3(aq) 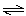 CO32-(aq) + NH4+(aq) CO32-(aq) + NH4+(aq) a. | HCO3- is an acid and NH3(aq) is its conjugate
base. | b. | HCO3- is an acid and
CO32- is its conjugate base. | c. | NH3
is an acid and HCO32- is its conjugate base. | d. | NH3
is an acid and NH4+ is its conjugate base. | e. | NH4+ is an acid and CO32- is its conjugate
base. | | |
|
|
|
50.
|
The
conjugate acid of OH- is a. | H3O+ | b. | H2O | c. | OH- | d. | O2- | e. | H- | | |
|
|
|
51.
|
What
is the conjugate acid of HPO42-(aq)? a. | H3PO4 | b. | H2PO4- | c. | PO42- | d. | H3O+ | e. | OH- | | |
|
|
|
52.
|
What
is the OH- concentration of a solution with a pH of 3.75? a. | 5.2 ´
10-13 M | b. | 5.6 ´ 10-11 M | c. | 4.9 ´ 10-7
M | d. | 1.8 ´ 10-4
M | e. | 3.8 ´ 10-2
M | | |
|
|
|
53.
|
Which
of the following chemical reactions corresponds to the base ionization constant,
Kb, for ammonia? a. | NH3(aq) + H2O(ª) 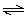 NH4+(aq) +
OH-(aq) NH4+(aq) +
OH-(aq) | b. | NH4+(aq) + H2O(ª) 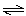 NH3(aq) +
H3O+(aq) NH3(aq) +
H3O+(aq) | c. | NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)  NH3(aq) + H2O(ª) NH3(aq) + H2O(ª) | d. | NH3(aq) + OH-(aq)  NH2-(aq) +
H2O(ª) NH2-(aq) +
H2O(ª) | e. | NH3(aq) + H3O+(aq)  NH4+(aq) +
H2O(ª) NH4+(aq) +
H2O(ª) | | |
|
|
|
54.
|
Which
of the following weak acids has the strongest conjugate base? a. | acetic acid,
Ka = 1.8 ´ 10-5 | b. | benzoic acid,
Ka = 6.3 ´ 10-5 | c. | dihydrogen
phosphate ion, Ka = 6.2 ´ 10-8 | d. | formic acid,
Ka = 1.8 ´ 10-4 | e. | hydrocyanic
acid, Ka = 4.0 ´ 10-10 | | |
|
|
|
55.
|
What
is the pH of a 0.050 M solution of formic acid? (Ka for HCO2H = 1.8
´
10-4) a. | 2.54 | b. | 2.91 | c. | 3.21 | d. | 4.07 | e. | 5.99 | | |
|
|
|
56.
|
What
is the pH of a 0.75 M solution of sodium cyanide, NaCN? (Kb for CN-
=
2.5 ´ 10-5) a. | 2.36 | b. | 4.33 | c. | 9.58 | d. | 10.04 | e. | 11.64 | | |
|
|
|
57.
|
Which
of the following chemical reactions corresponds to Ka2 for phosphoric
acid? a. | HPO42-(aq) + H2O(ª)  PO43-(aq) +
H3O+(aq) PO43-(aq) +
H3O+(aq) | b. | PO43-(aq) + H2O(ª) 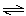 HPO42-(aq) +
OH-(aq) HPO42-(aq) +
OH-(aq) | c. | H3PO4(aq) + H2O(ª)  H2PO4-(aq) +
H3O+(aq) H2PO4-(aq) +
H3O+(aq) | d. | H3PO4(aq) + 2 H2O(ª)  HPO42-(aq) + 2
H3O+(aq) HPO42-(aq) + 2
H3O+(aq) | e. | H2PO4-(aq) +
H2O(ª)  HPO42-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
HPO42-(aq) + H3O+(aq) | | |
|
|
|
58.
|
What
is the pH of 0.50 M H3PO4? (Ka1 = 7.5 ´
10-3, Ka2 = 6.2 ´ 10-8, Ka3 = 3.6 ´
10-13) a. | 0.97 | b. | 1.24 | c. | 2.67 | d. | 5.15 | e. | 6.33 | | |
|
|
|
59.
|
Of
the following salts, which one forms a 0.1 M solution with the highest pH? a. | KCl | b. | NH4Cl | c. | FeCl3 | d. | KNO2 | e. | Ca(NO3)2 | | |
|
|
|
60.
|
All
of the following compounds are acids containing chlorine. Which compound is the weakest
acid? a. | HCl | b. | HClO | c. | HClO2 | d. | HClO3 | e. | HClO4 | | |
|
|
|
61.
|
We
have a solution of ammonia. What is the effect of adding ammonium chloride to this
solution?
1. The pH increases.
2. The
concentration of NH3 increases.
3. The
concentration of H3O+ increases
a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 2 and
3 | | |
|
|
|
62.
|
What
is the pH of a solution of 0.25 M acetic acid and 0.25 M sodium acetate? (Ka for
CH3CO2H = 1.8 ´ 10-5) a. | 0.60 | b. | 2.12 | c. | 2.67 | d. | 4.74 | e. | 5.32 | | |
|
|
|
63.
|
Which
of the following combinations would be the best to buffer the pH to 9.0? a. | H3PO4 and H2PO4-,
Ka = 7.5 ´ 10-3 | b. | HNO2
and NO2-, Ka = 4.5 ´ 10-4 | c. | CH3CO2H and CH3COO-, Ka
= 18 ´
10-5 | d. | H2PO4- and
HPO42-, Ka = 6.2 ´ 10-8 | e. | NH4+ and NH3, Ka = 5.7 ´
10-10 | | |
|
|
|
64.
|
All
of the following will produce a buffer solution EXCEPT a. | NH4Cl
and NH3. | b. | HCN and KCN. | c. | NaHCO3 and Na2CO3. | d. | NaH2PO4 and
Na2HPO4. | e. | NaOH and NaCl. | | |
|
|
|
65.
|
Which
of the following mathematical expressions is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation? a. | pH =
pKa + log | b. | pKa = pH + lo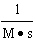 | c. | pH = pKa + log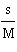 | d. | pKa = pH - log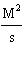 | e. | None of the above equations is
correct. | | |
|
|
|
66.
|
All
of the following statements concerning buffers are true EXCEPT a. | buffers are
resistant to changes in pH upon the addition of strong acids. | b. | buffers are
resistant to changes in pH when diluted with water. | c. | the pH of a
buffer is close to the pKa of the weak acid from which it is
made. | d. | buffers contain appreciable quantities of a weak acid and its
conjugate base. | e. | buffers are used as colored indicators in acid-base
titrations. | | |
|
|
|
67.
|
What
is the pH of a buffer that results when 0.50 mole of H3PO4 is mixed with 0.75
mole of NaOH and diluted with water to 1.00 L? (Ka1 = 7.5 ´
10-3, Ka2 = 6.2 ´ 10-8, Ka3 = 3.6 ´
10-13) a. | 7.21 | b. | 7.45 | c. | 8.01 | d. | 8.23 | e. | 9.91 | | |
|
|
|
68.
|
If
the ratio of base to acid in a buffer changes by a factor of 10, the pH of the
buffer a. | increases by
2. | b. | increases by
1. | c. | decreases by
1. | d. | decreases by
2. | e. | remains
unchanged. | | |
|
|
|
69.
|
Which
one of the following conditions is true for a titration of a weak acid with a strong
base? a. | The equivalence
point occurs at a pH greater than 7. | b. | The equivalence point occurs at a pH equal to
7. | c. | Equal volumes of
acid and base are required to reach the equivalence point. | d. | A colored
indicator with a pKa less than 7 should be used. | e. | The colored
indicator should change color rapidly in the buffer region. | | |
|
|
|
70.
|
Potassium hydrogen phthalate (molar mass = 204.2 g/mol) is used to standardize sodium
hydroxide. If 22.10 mL of NaOH is required to titrate 0.6103 g KHP to the equivalence point, what is
the concentration of the NaOH?
HC8H4O4-(aq) + OH-(aq)  C8H4O42-(aq) + H2O(ª)
C8H4O42-(aq) + H2O(ª)
a. | 0.06605 M | b. | 0.1352
M | c. | 0.1514
M | d. | 0.1617
M | e. | 0.2762
M | | |
|
|
|
71.
|
A
25.0 mL sample of vinegar is titrated with 0.0950 M NaOH. If the titration requires 35.8 mL of NaOH,
what is the concentration of acetic acid in the vinegar? a. | 0.0663
M | b. | 0.0971
M | c. | 0.136
M | d. | 0.329
M | e. | 0.727
M | | |
|
|
|
72.
|
Which
of the following equations is the solubility product for
Ca(IO3)2? a. | Ksp =
[Ca2+][I-]2[O2-]6 | b. | Ksp =
[Ca2+][I-]2[3O2-]2 | c. | Ksp = [Ca2+][IO ] ] | d. | Ksp = [Ca2+][IO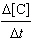 ]2 ]2 | e. | Ksp = [Ca2+]2[IO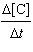 ] ] | | |
|
|
|
73.
|
The
solubility of BaSO4 is 1.05 ´ 10-5 mol/L. What is the value of Ksp for
BaSO4? a. | 3.24
´
10-3 | b. | 6.48 ´ 10-3 | c. | 2.10
´
10-5 | d. | 1.10 ´ 10-10 | e. | 2.20
´
10-10 | | |
|
|
|
74.
|
The
Ksp for BaF2 is 1.7 ´ 10-6. What is the concentration of Ba2+
in a saturated solution of BaF2? a. | 5.7 ´ 10-7 M | b. | 1.7 ´ 10-6
M | c. | 1.0 ´ 10-2
M | d. | 1.3 ´ 10-3
M | e. | 7.5 ´ 10-3
M | | |
|
|
|
75.
|
The
following anions can be separated by precipitation as silver salts: Cl-, Br-,
I-, CrO42-. If Ag+ is added to a solution containing the
four anions, each at a concentration of 0.10 M, in what order would they
precipitate?
Compound | Ksp | | AgCl | 1.8 ´ 10-10 | | Ag2CrO4 | 9.0 ´ 10-12 | | AgBr | 3.3 ´ 10-13 | | AgI | 1.5 ´ 10-16 | | | |
a. | AgCl®Ag2CrO4®AgBr®AgI | b. | AgI®AgBr®Ag2CrO4®AgCl | c. | Ag2CrO4®AgCl
AgBr®AgI | d. | Ag2CrO4®AgI
AgBr®AgCl | e. | AgI®AgBr®AgCl®Ag2CrO4 | | |
|
|
|
76.
|
If
the reaction A + B 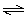 C has an equilibrium constant greater than one,
which of the following statements is correct? C has an equilibrium constant greater than one,
which of the following statements is correct? a. | The reaction is not spontaneous. | b. | The forward rate
of reaction is fast. | c. | The backward rate of reaction is
slow. | d. | The reaction is product favored. | e. | All of the above
statements are correct. | | |
|
|
|
77.
|
If a
chemical reaction has a positive change in entropy, S, then a. | the disorder of
the system increases. | b. | the reaction is exothermic. | c. | heat goes from
the system into the surroundings. | d. | the Gibbs free energy is negative. | e. | the reaction is
spontaneous. | | |
|
|
|
78.
|
Thermodynamics can be used to determine all of the following EXCEPT a. | the direction in
which a reaction is spontaneous. | b. | the extent to which a reaction
occurs. | c. | the rate of reaction. | d. | the temperature
at which a reaction is spontaneous. | e. | the enthalpy change of a reaction. | | |
|
|
|
79.
|
A
statement of the second law of thermodynamics is that a. | spontaneous
reactions are always exothermic. | b. | energy is conserved in a chemical
reaction. | c. | the entropy of the universe is continually
increasing. | d. | the enthalpy of reaction is the difference between product and
reactant enthalpies. | e. | the Gibbs free energy is a function of both enthalpy and
entropy. | | |
|
|
|
80.
|
Of
the following product-favored processes, which are endothermic?
1. the combustion of methane to produce water and carbon
dioxide
2. the expansion of an ideal gas
3. the melting
of ice at temperatures greater than 0ºC. a. | 1 only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 2 and
3 | | |
|
|
|
81.
|
All
of the following processes lead to an increase in entropy EXCEPT a. | increasing the
temperature of a gas. | b. | freezing a liquid. | c. | evaporating a
liquid. | d. | forming mixtures from pure
substances. | e. | chemical reactions that increase the number of moles of
gas. | | |
|
|
|
82.
|
Predict the signs of DH and DS for the evaporation of water at 35ºC. a. | DH > 0 and DS > 0 | b. | DH > 0 and DS < 0 | c. | DH < 0 and DS > 0 | d. | DH < 0 and DS < 0 | e. | Not enough
information is provided to answer this question. | | |
|
|
|
83.
|
Predict the signs of DH, DS, and DG for the combustion of hydrogen gas at 25ºC.
2 H2(g) + O2(g) ® 2
H2O(ª)
a. | DH < 0, DS < 0, DG < 0 | b. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | c. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | d. | DH > 0, DS < 0, DG < 0 | e. | DH > 0, DS < 0, DG > 0 | | |
|
|
|
84.
|
Predict the signs of DH, DS, and DG for the melting of ice at 50ºC. a. | DH < 0, DS < 0, DG < 0 | b. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | c. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | d. | DH > 0, DS < 0, DG < 0 | e. | DH > 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | | |
|
|
|
85.
|
If
DG < 0
for a reaction at all temperatures, then DS is ________ and DH is ________. a. | positive, positive | b. | positive,
negative | c. | zero, positive | d. | negative,
positive | e. | negative, zero | | |
|
|
|
86.
|
The
dissolution of ammonium nitrate occurs spontaneously in water. As NH4NO3
dissolves, the temperature of the water decreases. What are the signs of H, S, and
G for this process? a. | DH < 0, DS < 0, DG < 0 | b. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | c. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | d. | DH > 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | e. | DH > 0, DS < 0, DG > 0 | | |
|
|
|
87.
|
All
of the following relationships are true EXCEPT a. | | b. | DG = - RT
1n(K) = - RT
1n(K) | c. | | d. | DH = DH + RT
1n(K) + RT
1n(K) | e. | DG -
TDS -
TDS | | |
|
|
|
88.
|
At
what temperature would you expect a reaction to become spontaneous if DH = +67.0
kJ and DS = -131
J/K? a. | T <
-511 K | b. | T > 238 K | c. | T >
511 K | d. | The reaction will be spontaneous at any
temperature. | e. | The reaction will NOT be spontaneous at any
temperature. | | |
|
|
|
89.
|
Calculate  for the
reaction below at 25.0ºC for the
reaction below at 25.0ºC
2
H2O2(ª) ® 2 H2O(ª) + O2(g)
given DG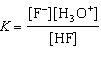 [H2O2(ª)] = -120.35 kJ/mol, DG [H2O2(ª)] = -120.35 kJ/mol, DG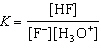 [H2O(ª)] = -237.13 kJ/mol, DG
[H2O(ª)] = -237.13 kJ/mol, DG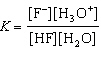 [O2(g)] = 0 kJ/mol. [O2(g)] = 0 kJ/mol.
a. | 714.96 kJ | b. | 543.91
kJ | c. | -438.23
kJ | d. | -233.56
kJ | e. | -67.03
kJ | | |
|
|
|
90.
|
If
DGº< 0, then a. | K >1 | b. | K =
0 | c. | K <
1 | d. | K =
1 | e. | K <
0 | | |
|
|
|
91.
|
For a
chemical system, DGº and DG are equal when a. | the equilibrium constant, K, equals
1. | b. | the equilibrium
constant, K, equals 0. | c. | a system is at equilibrium. | d. | the reactants
and products are in standard state concentrations. | e. | the reactant and
products are in the gas phase. | | |
|
|
|
92.
|
The
equilibrium constant for a reaction at 298 K is 9.3 ´ 10-12. What is DGº?
(R = 8.314 J/Kmol) a. | 2.54 kJ | b. | +2.54
kJ | c. | +5.28
kJ | d. | +62.9
kJ | e. | +87.1
kJ | | |
|
|
|
93.
|
Given
that
C(s) +
O2(g) ® CO2(g) | DGº =
-394.4 kJ | CO(g) + O2(g) ®
CO2(g) | DGº = -257.2 kJ | | |
calculate
DGº
for the following reaction.
C(s) +
O2(g)® CO(g) a. | 651.6 kJ | b. | 137.2
kJ | c. | +1.53
kJ | d. | +45.3
kJ | e. | +651.6
kJ | | |
|
|
|
94.
|
Calculate for CaCO3 given the following
information.
C(s) +
O2(g) ® CO2(g) | DGº =
-394.4 kJ | CaO(g) + CO2(g) ® CaCO
3(s) | DGº = -130.4 kJ | Ca(s) +
O2(g) ® CaO(s) | DGº = -604.0 kJ | | |
a. | 1128.8 kJ | b. | 340.0
kJ | c. | 130.4
kJ | d. | +868.0
kJ | e. | +1128.8
kJ | | |
|
|
|
95.
|
The
following reaction occurs spontaneously.
2 H+(aq) + Ca(s) ® Ca2+(aq) +
H2(g)
Write the balanced oxidation
half-reaction. a. | 2
H+(aq) + 2 e- ® H2(g) | b. | 2
H+(aq) ® H2(g) + 2 e- | c. | 2
H+(aq) + Ca(s) ® 2 e- | d. | Ca(s) + 2
e- ® Ca2+(aq) | e. | Ca(s)
®
Ca2+(aq) + 2 e- | | |
|
|
|
96.
|
The
following reaction occurs spontaneously,
3 Cu2+(aq) + 2 Fe(s) ® 2
Fe3+(aq) + 3 Cu(s)
Write the
balanced reduction half-reaction. a. | 2 Fe(s) ® 2 Fe3+(aq) + 6
e- | b. | 2 Fe(s) + 6 e- ® 2
Fe3+(aq) | c. | 3 Cu2+(aq) + 6 e- ® 3
Cu(s) | d. | 3 Cu2+(aq) ® 3 Cu(s) + 6 e- | e. | 3
Cu2+(aq) + 2 Fe(s) + 6 e- ® 3Cu(s) + 2 Fe3+(aq) | | |
|
|
|
97.
|
Write
a balanced half-reaction for the oxidation of water. a. | 2
H2O(ª) ® O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) + 4
e- | b. | 2 H2O(ª) ® H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) + 2
e- | c. | H2O(ª) + 2 e- ® H2(g) + 2
OH-(aq) | d. | 2 H2O(ª) + 2 e- ® H2O2(aq) + 2
H2(g) | e. | 2 H2O(ª) ® 2 H2(g) + O2(g) + 4
e- | | |
|
|
|
98.
|
Write
a balanced half-reaction for the reduction of NO3-(aq) to NO(g) in an acidic
solution. a. | NO3-(aq) + H+(aq) + e- ® NO(g) +
HO2(aq) | b. | NO3-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) +
e- ® NO(g) + 2 OH-(aq) | c. | NO3-(aq) + 3 e- ® NO(g) + 2
O2(g) | d. | NO3-(aq) + 4 H+(aq) + 3
e- ® NO(g) + 2 H2O(ª) | e. | 2 HNO3(aq) + 6 e- ® NO(g) +
H2(g) + 3 O2(g) | | |
|
|
|
99.
|
Write
a balanced chemical equation for the following reaction in an acidic
solution.
Cr2O72-(aq) +
Fe2+(aq) ® Cr3+(aq) + Fe3+(aq)
a. | Cr2O72-(aq) + Fe2+(aq) ® 2
Cr3+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) | b. | Cr2O72-(aq) +
Fe2+(aq) + 7 H+(aq) ® 2 Cr3+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) + 7
OH-(aq) | c. | Cr2O72-(aq) + 6
Fe2+(aq) + 7 H+(aq) ® 2 Cr3+(aq) + 6 Fe3+(aq) + 7
OH-(aq) | d. | Cr2O72-(aq) +
Fe2+(aq) + 14 H+(aq) ® 2 Cr3+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) + 7
H2O(ª) | e. | Cr2O72-(aq) + 6
Fe2+(aq) + 14 H+(aq) ® 6 Fe3+(aq) + 2 Cr3+(aq) + 7
H2O(ª) | | |
|
|
|
100.
|
All
of the following statements concerning voltaic cells are true EXCEPT a. | the two
half-cells are connected by a salt bridge. | b. | electrons flow from the anode to the
cathode. | c. | oxidation occurs at the cathode. | d. | voltaic cells
can be used as a source of energy. | e. | a voltaic cell consists of two-half
cells. | | |
|
|
|
101.
|
What
is the correct cell notation for the reaction below?
Cu2+(aq) + Pb(s) ® Cu(s) + Pb2+(aq)
a. | Pb |
Pb2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu | b. | Pb |
Cu2+(aq) || Pb2+(aq) | Cu | c. | Pb | Cu(s) ||
Pb2+(aq) | Cu2+ | d. | Cu | Pb2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) |
Pb | e. | Cu |
Cu2+(aq) || Pb2+(aq) | Pb | | |
|
|
|
102.
|
Write
a balanced chemical equation for the overall reaction represented by the cell notation
below.
Pt | H2(g) | H+(aq) |
Cl-(aq) | Cl2(g) | Pt a. | 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) ®
H2(g) + Cl2(g) | b. | Pt + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) ®
H2(g) + Cl2(g) + Pt | c. | 2 Cl2(g) + 4 H+(aq) ®
PtCl4(aq) + 2 H2(g) | d. | Cl2(g) + H2(g) ® 2
Cl-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) | e. | Cl2(g) + 2 H+(aq) ® 2
Cl-(aq) + H2(g) | | |
|
|
|
103.
|
Consider the following half-reactions:
Fe3+(aq) + e- ® Fe2+(aq) | Eº = +0.77 V | Sn2+(aq) + 2 e- ® Sn(s) | Eº =
-0.14 V | Fe2+(aq) + 2 e- ® Fe(s) | Eº =
-0.44 V | Al3+(aq) + 3 e- ® Al(s) | Eº =
-1.66 V | Mg2+(aq) + 2 e- ® Mg(s) | Eº =
-2.37 V | | |
Which of the above metals or metal ions are able to oxidize
Al(s)? a. | Fe3+
and Sn2+ | b. | Fe3+, Sn2+, and
Fe2+ | c. | Fe2+, Sn, and Fe | d. | Mg and
Mg2+ | e. | Mg2+ only | | |
|
|
|
104.
|
Given
the following two half-reactions, determine which overall reaction is spontaneous and calculate the
cell potential.
Mg2+(aq) + 2 e- ® Mg(s) | Eº =
-2.37 V | Ni2+(aq) + 2 e- ® Ni(s) | Eº =
-0.25 V | | |
a. | Mg2+(aq) + Ni(s) ® Mg(s) +
Ni2+(aq) E = +2.12 V = +2.12 V | b. | Mg2+(aq) + Ni(s) ® Mg(s) +
Ni2+(aq) E = -2.62 V = -2.62 V | c. | Mg2+(aq) + Ni2+(aq) ® Mg(s) +
Ni(s) E = +2.62 V = +2.62 V | d. | Mg(s) + Ni2+(aq) ® Ni(s) +
Mg2+(aq) E = +2.12 V = +2.12 V | e. | Mg2+(aq) + Ni2+(aq) ® Ni(s) +
Mg(s) E = -2.12 V = -2.12 V | | |
|
|
|
105.
|
Calculate E for the
following electrochemical cell: for the
following electrochemical cell:
Pt |
H2(g) | H+(aq) || Pb2+(aq) | PbSO4(s) |
Pb
given the following standard reduction
potentials.
2 H+(aq) + 2 e- ® H2(g) | Eº = 0.000 V | PbSO4(s) + 2 e- ® Pb(s) + SO 42-(aq) | Eº = -0.356 V | | |
a. | -0.712
V | b. | -0.356
V | c. | -0.178
V | d. | +0.356
V | e. | +0.712
V | | |
|
|
|
106.
|
Which
one of the changes below will increase the potential of the following electrochemical
cell?
Pt | Sn4+(aq, 1.0 M), Sn2+(aq,
1.0 M) || Cu2+(aq, 0.200 M) | Cu a. | Switching from a platinum to a graphite
anode. | b. | Increasing the size of the cathode. | c. | Decreasing the
concentration of Cu2+. | d. | Increasing the concentration of
Sn2+. | e. | Increasing the temperature of the
cell. | | |
|
|
|
107.
|
Calculate  for the
disproportionation of Cu+, for the
disproportionation of Cu+,
2 Cu+(aq) ® Cu2+(aq) + Cu(s)
given the following standard reduction
potentials.
Cu+(aq) + e- ® Cu(s) | Eº =
+0.518 V | Cu2+(aq) + 2 e- ® Cu(s) | Eº =
+0.337 V | | |
a. | -1180
kJ | b. | -175
kJ | c. | -165
kJ | d. | -56.8
kJ | e. | -34.9
kJ | | |
|
|
|
108.
|
If
 for the following reaction is -1.73 ´ 103
J, calculate for the following reaction is -1.73 ´ 103
J, calculate  . .
Cr2O72-(aq) + 2 Al(s) + 14
H+(aq) ® 2 Cr3+(aq) + 2 Al3+(aq) + 7
H2O(ª)
a. | +1.49 V | b. | +2.18
V | c. | +2.99
V | d. | +4.48
V | e. | +5.98
V | | |
|
|
|
109.
|
What
is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25ºC?
Ni(s) + Cd2+(s) ® Ni2+(aq) +
Cd(s)  = -0.15
V = -0.15
V
a. | 2.1 ´
10-12 | b. | 8.4 ´ 10-6 | c. | 1.0 ´
10-1 | d. | 1.2 ´ 101 | e. | 1.2 ´
105 | | |
|
|
|
110.
|
What
charge, in coulombs, is required to deposit 0.205 g Ag(s) from a solution of
Ag+(aq)? a. | 2.29 C | b. | 54.6
C | c. | 103
C | d. | 183
C | e. | 197
C | | |
|
|
|
111.
|
The
least penetrating type of radiation can be stopped by clothing or a few pieces of paper. This type of
radiation is a(n) a. | alpha
particle. | b. | beta particle. | c. | gamma
particle. | d. | positron. | e. | cathode
ray. | | |
|
|
|
112.
|
Which
one of the following symbols is used to represent gamma ray emission?
|
|
|
113.
|
Which
of the following reactions is an example of beta particle emission?
|
|
|
114.
|
The
atomic number of a nucleus that undergoes electron capture will a. | decrease by two
units. | b. | decrease by one unit. | c. | remain the
same. | d. | increase by one unit. | e. | increase by two
units. | | |
|
|
|
115.
|
The
mass number of a nucleus that emits an alpha particle will a. | decrease by four
units. | b. | decrease by two units. | c. | remain the
same. | d. | increase by two units. | e. | increase by two
units. | | |
|
|
|
116.
|
What
particle is produced in the following reaction?
|
|
|
117.
|
Strontium-90 has a half-life of 28.1 years. Starting with 3.2 mg of this isotope, how
much would remain after 112.4 years? a. | 0.1 mg | b. | 0.2
mg | c. | 0.4
mg | d. | 0.8
mg | e. | 1.6
mg | | |
|
|
|
118.
|
What
do scientists call the sequence of rapidly occurring reactions that results when a nuclear fission
reaction produces enough neutrons to produce more fission reactions? a. | nuclear
fusion | b. | nuclear fission | c. | chain
reaction | d. | neutron emission | e. | binding
energy | | |
|
|
|
119.
|
Enriched uranium is uranium that has a greater proportion of a. | lead-207. | b. | radium-226. | c. | uranium-235. | d. | uranium-238. | e. | plutonium-248. | | |
|
|
|
120.
|
What
role do the cadmium control rods play in a fission reactor? a. | They emit
electrons which initiate the fission reaction. | b. | The cadmium
combines with spent uranium fuel to produce a non-radioactive product. | c. | They focus the
neutrons toward the center of the reactor. | d. | The cadmium acts as a catalyst, enabling fission to occur at
lower temperatures. | e. | They control the rate of fission by absorbing
neutrons. | | |
|
|
|
121.
|
All
of the following statements regarding isomers are correct EXCEPT a. | optical isomers
have non-superimposable mirror images. | b. | there are two types of stereoisomers, geometric and optical
isomers. | c. | enantiomers are pairs of non-superimposable
molecules. | d. | enantiomers have different physical properties, such as melting
point and color. | e. | molecules with non-superimposable mirror images are said to be
chiral. | | |
|
|
|
122.
|
How
many structural isomers exist for C5H12?
|
|
|
123.
|
Which
of the following (non-cyclic) hydrocarbons has at least two p bonds? a. | C4H8 | b. | C10H20 | c. | C8H18 | d. | C5H12 | e. | C3H4 | | |
|
|
|
124.
|
What
is the name of the following compound?
a. | 4,5-dihexane | b. | 2,3-diethylhexane | c. | 4,5-dimethane | d. | 2,3-dimethylhexane | e. | 4,5-dimethylhexane | | |
|
|
|
125.
|
What
is the name of the following compound?
a. | 3-methyl-5-ethylheptane | b. | 3,5-diethylhexane | c. | 2-methyl-4-ethylpentane | d. | 2,4-diethylhexane | e. | 5-ethyl-3-methylheptane | | |
|
|
|
126.
|
What
is the name of the following compound?
a. | cis-4-propyl-3-butene | b. | ethyl-propylethene | c. | cis-ethyl-propylethene | d. | cis-3-heptene | e. | cis-5-ethyl-4-pentene | | |
|
|
|
127.
|
What
is the name of the following compound?
a. | 4-methyl-2-pentyne | b. | 4,4-dimethylbutyne | c. | 4,4-dimethyl-2-butyne | d. | 2-methyl-3-pentyne | e. | 2-methyle-3,4-pentadyne | | |
|
|
|
128.
|
Which
of the following compounds are aromatic?
a. | 3
only | b. | 1 and
4 | c. | 2
only | d. | 1, 2, and
4 | e. | 4
only | | |
|
|
|
129.
|
How
many isomers are possible for dichlorotoluene? Toluene is a benzene ring with a single methyl
substituent.
|
|
|
130.
|
What
is the name of the following benzene derivative?
a. | 3-chlorobenzoic
acid | b. | 2-chlolobenzoic
acid | c. | 1-nitro-3-chlorobenzene | d. | 1-carbonate-3-chlorobenzene | e. | 3-chlorotoluene | | |
|
|
|
131.
|
Which
functional group does not contain an oxygen atom? a. | alcohol | b. | amine | c. | amide | d. | ester | e. | ether | | |
|
|
|
132.
|
The
functional group RCOR' is characteristic of an ________. a. | ester | b. | alcohol | c. | amine | d. | aldehyde | e. | amide | | |
|
|
|
133.
|
The
C=O linkage occurs in molecules with the following functional groups EXCEPT
________. a. | esters | b. | ketones | c. | amines | d. | carboxylic acids | e. | aldehydes | | |
|
|
|
134.
|
What
is the product of the reaction of an aldehyde with potassium dichromate? a. | ketone | b. | alcohol | c. | ester | d. | alkane | e. | carboxylic
acid | | |
|
|
|
135.
|
What
class of compounds is responsible for many of the distinctive odors of artificial flavors and
perfumes? a. | esters | b. | ethers | c. | aldehydes | d. | amides | e. | amines | | |
|
|
|
136.
|
What
is the monomer of Teflon? a. | CH2CH2 | b. | CHFCHF | c. | CF2CH2 | d. | CF2CF2 | e. | CHFCF2 | | |
|
|
|
137.
|
All
of the following statements concerning polymers are correct EXCEPT a. | elastomers are
materials that spring back to their original shape when stretched. | b. | polymers formed
from two or more different monomers are called copolymers. | c. | thermoplastics
can withstand very high temperatures without softening or melting. | d. | polystyrene is
nonpolar and dissolves well in nonpolar solvents. | e. | a condensation
reaction involves two different monomers, each with two different functional
groups. | | |
|
|
|
138.
|
Amino
acids polymerize in condensation reactions that result in the formation of an amide linkage (or
peptide bond. between amino acid molecules. What is a possible dipeptide formed in the reaction of
glycine with phenylalanine?
a. | Figure
a | b. | Figure
b | c. | Figure
c | d. | Figure
d | e. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
139.
|
Polyethylene a. | is an example of a condensation
polymer. | b. | reacts with methanol to form Dacron. | c. | contains no
double bonds. | d. | contains equal numbers of cis and trans
bonds. | e. | cannot form branched chains. | | |
|
|
|
140.
|
Polypropylene is used in bottles, carpet, and films. It is produced by the addition
reaction of propylene (propene). What is the structure of the polymer produced in this
reaction?
a. | Figure
a | b. | Figure
b | c. | Figure
c | d. | Figure
d | e. | Figure
e | | |
|