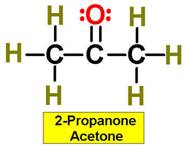
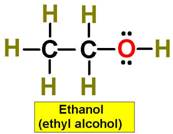
Path 4 Chapter 12 Study
Pack Name: __________________
Chapter 12: Introduction to Organic Chemistry
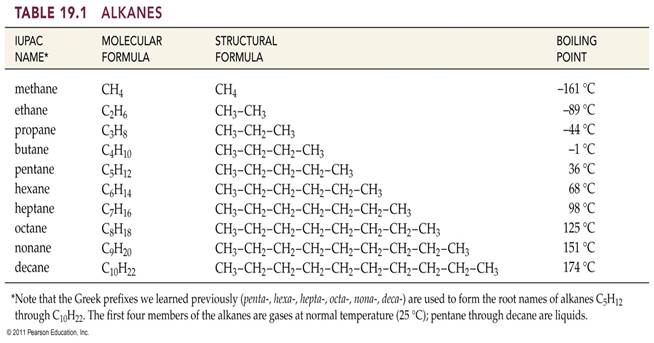
A. ______ Alkane Series Table 19.1 p 445 Answers
B. ______ Alkyl
Radicals Table 19.2 p 449 Answers
C. ______ Structural Isomer
Problem Section
D. ______ Recognition
of 1o, 2o, 3o, 4o carbons ( 0o,
1o,
2o,
3o
, 4o)
& hydrogen Answers
E. ______ Nomenclature
of Alkanes and
Cycloalkanes Answers
F. ______ Functional
Group Recognition Answers
Chapter
19
In Class/Take-Home Lab Structural Isomer Number Problems
______ (01) Structural Isomer Take-Home Problem #1 C6H14 (makeup-See #7)
______ (03) Structural Isomer Take-Home Problem #2 C7H16 (makeup C8H18)
______ (03) Structural Isomer Take-Home Problem #3 C5H11Br (makeup C6H13Br)
______ (03)
Structural Isomer Take-Home Problem #4 C4H8Br2 (makeup
C5H10Br2)
______ (03) Structural Isomer Take-Home Problem #5 C6H12 Cycloalkanes only (makeup C7H14)
______ (03) Structural Isomer Take-Home Problem #6 C6H12 Alkenes only (makeup C7H14)
______ (02) Makeup Structural Isomer Take-Home Problem C4H10O Alcohols & Ethers
________(18) Module
16 Take-Home Lab Total
Conceptual Chemistry 5th
Edition John Suchocki
Table of Contents .
Chapter 20
Organic Compounds
Links to Videos for each Chapter section:
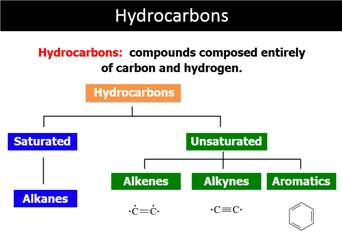
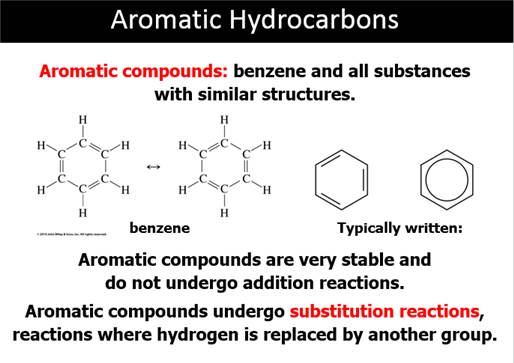
12.1 Hydrocarbons
Contain Only Carbon
and Hydrogen
12.2 Unsaturated
Hydrocarbons Have
Multiple Bonds
12.3 Functional
Groups Give Organic
Compounds Character
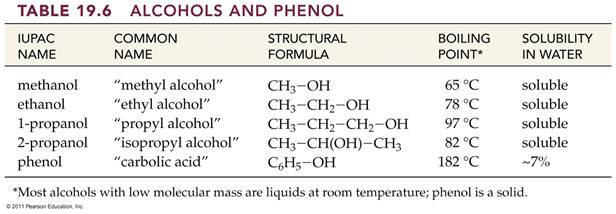
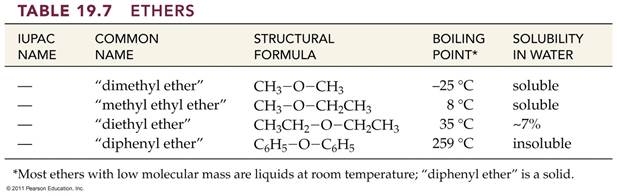
12.4 Alcohols,
Phenols, and Ethers
Contain Oxygen
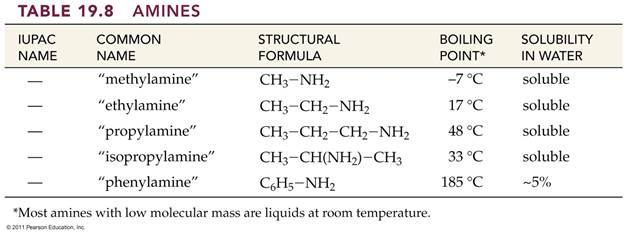
12.5 Amines
and Alkaloids Contain Nitrogen
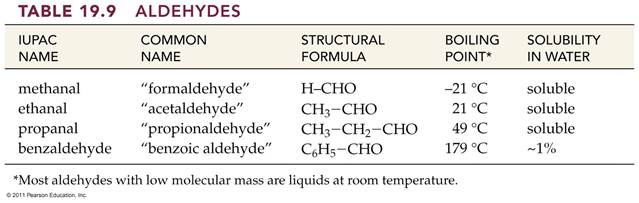
12.6 Carbonyl
Containing Compounds
12.7 An
Example of Organic Synthesis
12.8 Organic
Molecules Can Link to
Form Polymers
12.9 A
Brief History of Plastics
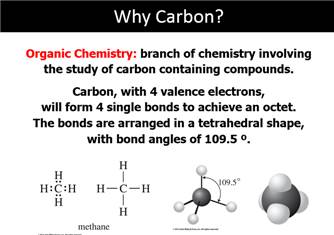



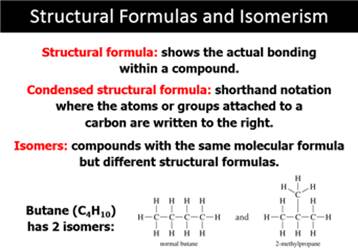
Chapter 12 Part A: Alkane Series
Name the first
ten members of the alkane series and give its chemical, semi-structural, or
structural formula:
Name
Chemical Formula
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Answers: http://www.lsua.us/chem1001/sampletest/20M16aAnswer.htm
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part B continued
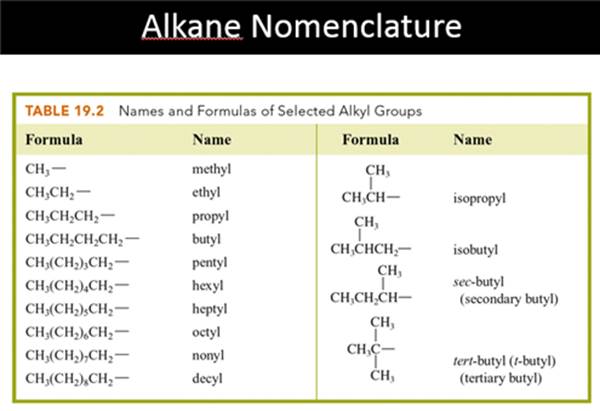
Chapter 12 Part B: Alkyl Radicals
Draw the
structural or semi-structural formulas for all the alkyl radicals of the first
four members of the alkane series, insert a X in place of the hydrogen which is
removed to make the radical:
Methyl Ethyl
n-propyl isopropyl
n-butyl sec-butyl
Isobutyl t-butyl
or tert-butyl
Answers: http://www.lsua.us/chem1001/sampletest/20M16bAnswer.htm
Chapter 12 Part B1: Additional Alkyl and Aryl Radicals
Draw the structural or semi-structural formulas for all the alkyl/aryl radicals of the following. Place a X in place of the hydrogen which is removed to make the radical: (Not in Textbook)
n-pentyl (amyl) isopentyl or isoamyl
neopentyl sec-amyl or sec-pentyl
Allyl vinyl
Benzyl phenyl
o-tolyl m-tolyl p-tolyl
CHM 1020 Chapter 12 Homework Pack
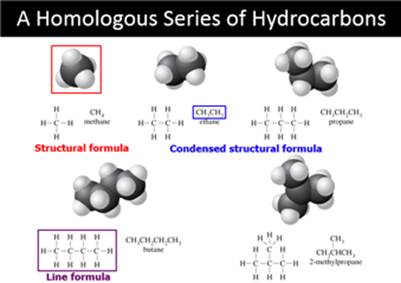


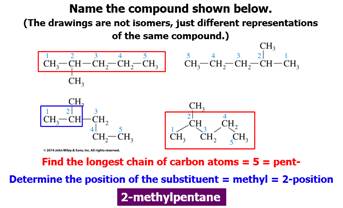
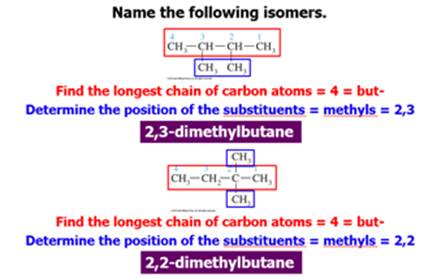

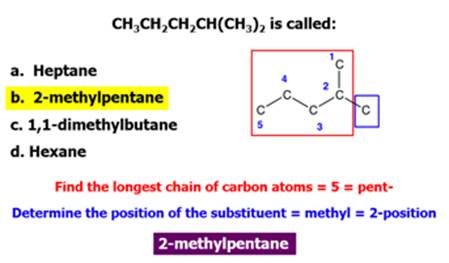


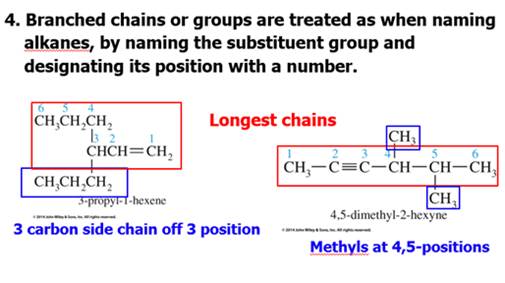
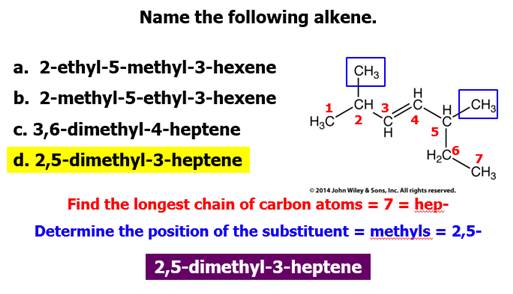
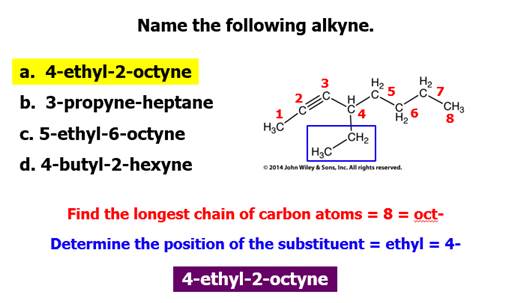

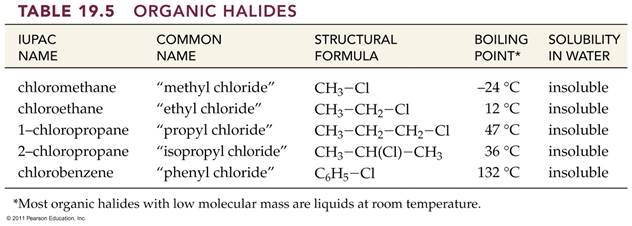
Chapter 12 Part C: Structural Isomer
Number Problem:
Alkanes, Alkyl halides, and Cycloalkanes
Draw the
structural or semi-structural formulas for all the isomers of the following
chemical formulas, then give the IUPAC name for each: (Use additional paper)
Test Item #1 C6H14
5 isomers;
Download Real Player
and then Download Hexane Isomer Video:
http://www.fccj.info/chem2414/isomers/Hexane_Isomers.rm
Test Item #2 C5H12 and
C4H10 5 total isomers between the two alkanes
Web Page: Structure and Nomenclature of
Hydrocarbons:
http://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/1organic/organic.html
Naming Organic Compounds: http://www2.chemistry.msu.edu/faculty/reusch/VirtTxtJml/nomen1.htm
IUPAC
Rules for Alkane Nomenclature
1. Find and name the longest continuous carbon
chain.
2. Identify and name groups attached to this chain.
3. Number the chain consecutively, starting at the end
nearest a substituent group.
4. Designate the location of each substituent group by an
appropriate number and name.
5. Assemble the name, listing groups in alphabetical order
using the full name (e.g. cyclopropyl before isobutyl).
The prefixes di, tri, tetra etc., used to designate several
groups of the same kind, are not considered when alphabetizing.
Test Item#3 C4H9Br 4 isomers;
Directions take
four butyl radicals in Part B and replace the X with Bromine and name the alkyl
bromides using the IUPAC
Test Item#4 C3H6Br2
4 isomers;
Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes
have one or more rings of carbon atoms. The simplest examples of this class
consist of a single, unsubstituted carbon ring, and these form a homologous
series similar to the unbranched alkanes. The IUPAC names of the first five
members of this series are given in the following table. The last (yellow
shaded) column gives the general formula for a cycloalkane of any size. If a
simple unbranched alkane is converted to a cycloalkane two hydrogen atoms, one
from each end of the chain, must be lost. Hence the general formula for a
cycloalkane composed of n carbons is CnH2n. Although a cycloalkane has
two fewer hydrogens than the equivalent alkane, each carbon is bonded to four
other atoms so such compounds are still considered to be saturated with
hydrogen.
Examples of Simple Cycloalkanes
|
||||||
|
Name |
Cyclopropane |
Cyclobutane |
Cyclopentane |
Cyclohexane |
Cycloheptane |
Cycloalkane |
|
Molecular |
C3H6 |
C4H8 |
C5H10 |
C6H12 |
C7H14 |
CnH2n |
|
Structural |
|
|
|
|
|
(CH2)n |
|
Line |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Substituted
cycloalkanes are named in a fashion very similar to that used for naming
branched alkanes. The chief difference in the rules and procedures occurs in
the numbering system. Since all the carbons of a ring are equivalent (a ring
has no ends like a chain does), the numbering starts at a substituted ring
atom.
IUPAC
Rules for Cycloalkane Nomenclature
1. For a monosubstituted cycloalkane the ring
supplies the root name (table above) and the substituent group is named as
usual. A location number is unnecessary. |
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part C continued
Test Item #5 C4H8
5 total isomers (cycloalkanes
plus alkenes) 1 Point No
Makeup
Test Item #6 C5H10 5 isomers (cycloalkanes only);
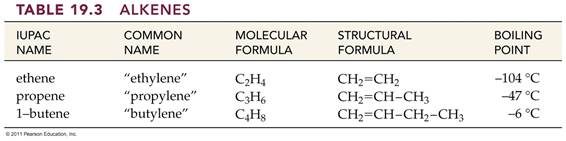
Read Guidelines for Naming Alkenes:
IUPAC
Rules for Alkene and Cycloalkene Nomenclature
1. The ene suffix (ending) indicates an
alkene or cycloalkene.
2. The longest chain chosen for the root name must include both
carbon atoms of the double bond.
3. The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest
a double bond carbon atom. If the double bond is in the center of the
chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where
numbering starts.
4. The smaller of the two numbers designating the carbon
atoms of the double bond is used as the double bond locator. If more than one
double bond is present the compound is named as a diene, triene or equivalent
prefix indicating the number of double bonds, and each double bond is assigned
a locator number.
5. In cycloalkenes the double bond carbons are assigned
ring locations #1 and #2. Which of the two is #1 may be determined by the
nearest substituent rule.
6. Substituent groups containing double bonds are:
H2C=CH– Vinyl group
H2C=CH–CH2– Allyl group
Test Item #7: C5H10
5 isomers (alkenes only)
Test Item #8 C6H4Br2
3 aromatic isomers
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part C continued
Problem #2 C7H16 9 isomers (makeup C8H18)
Hint: Parent: one heptane; two hexanes; five pentanes; and one butane
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part C continued
Problem #3 C5H11Br 8 isomers (makeup C6H13Br)
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part C continued
Problem #4: C4H8Br2 9
isomers (makeup C5H10Br2)
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part C continued
Problem#5 C6H1213 isomers (Cycloalkanes only (makeup C7H14)
CHM 1020
Chapter 12 Study Pack-Part C continued
Problem #6 C6H12 11isomers (alkenes only) (makeup C7H14)
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part D continued
Chapter 12 Part D:
Recognition of 1o, 2o, 3o,
4o carbons & 1o, 2o, 3o
hydrogen
Classify
the carbon or hydrogen atom in the below structure as 1o,
2o, 3o, 4o
or primary, secondary, tertiary, or neo (or
quaternary) carbon or hydrogen atoms:
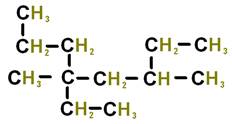
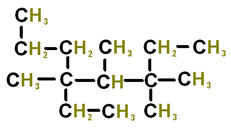
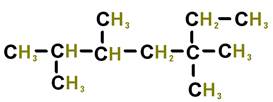
The numbers below on each image refer to the parent hydrocarbon of the chain::
|
Image #2
Iamge#3
Image#4
|
Image#1 1.
C1:_____ 2.
C2: _____ 3.
H2: _____ 4.
C4: _____ 5.
C5 :_____ 6.
C6: _____ Image#2 7.
C5: _____ 8. C3:_____ 9. C2:_____ 10.
C1:_____ Image#3 11.
C5:_____ 12.
C4:_____ 13.
H3_____ 14.
C2:_____ 15.C1:
_____ Image#4 16.
C5:_____ 17.
H4:_____ 18.
C3:_____ 19.
C2:_____ 20.
C1:_____ |
No Reading Reference: See Notes from
Lecture/See Web Site Links
0o; 1o; 2o;
3o; 4o Carbon Atoms :Methyl/Primary
Carbon Atoms Secondary
Carbon Atom Tertiary Carbon
Atoms Neo Carbon
Atoms
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part E continued
Chapter 12 Part E: Nomenclature of Alkanes and
Cycloalkanes
Give the IUPAC
Name for the following compounds:
|
1.
___________________________ |
|
|
2.
___________________________ |
|
|
3.
____________________________ |
|
|
4.
___________________________ |
|
|
5.
___________________________ |
|
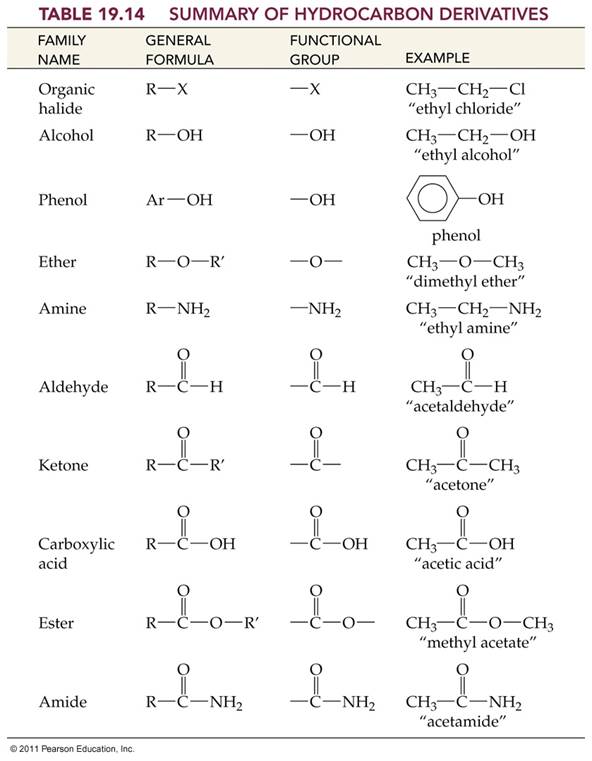
Classification of Organic Compounds Via Functional
Groups
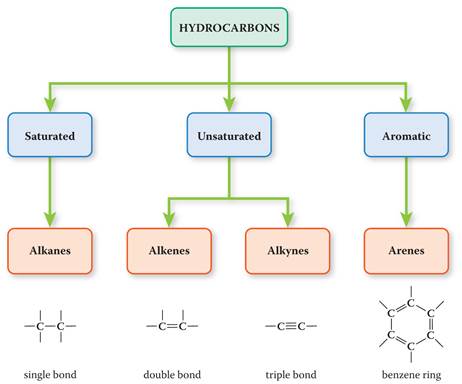
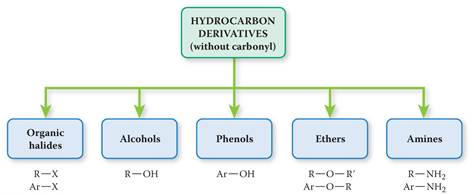
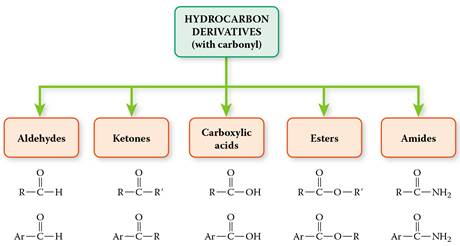
CHM 1020 Chapter 12
Study Pack-Part F continued
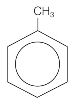
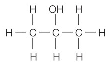
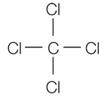
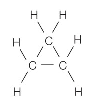
Chapter 12 Part F:
Functional Group Recognition
Classify the
following compounds according to their Functional Group:
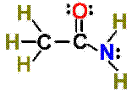
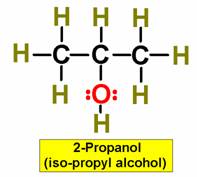
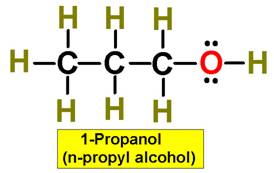
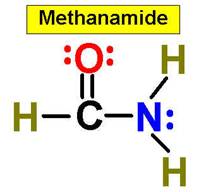
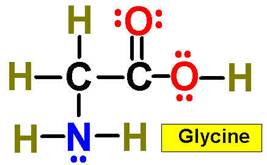
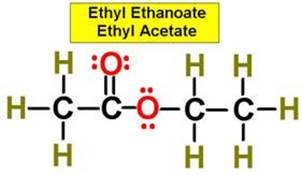
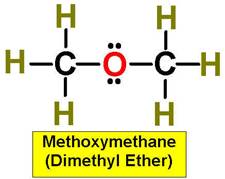
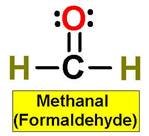
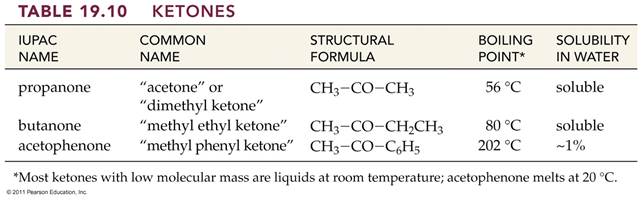
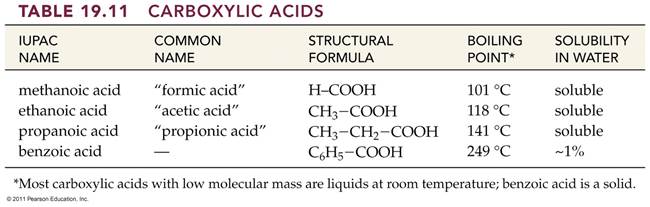
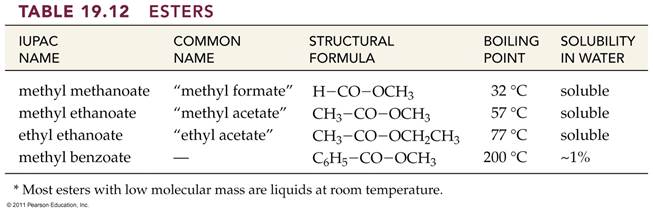
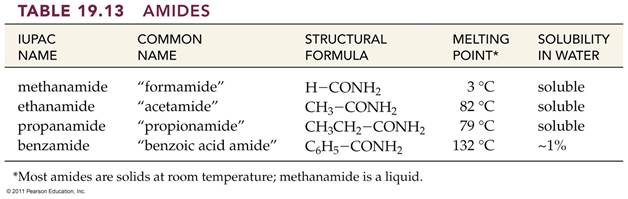
A. Alkane F. Aromatic Hydrocarbon K. Ketone P. Amide
B. Alkene G. Alkyl/Aryl Halide L. Carboxylic
Acid
C. Alkyne H. Alcohol M. Ester
D. Cycloalkane I. Ether N. Amine
E. Cycloalkene J. Aldehyde O. Amino Acid
|
1. ___ 2. ___ 3. ___ 4. ___ 5. ___ 6. ___ 7. ___ 8. ___ 9. ___ 10. __ 11. __ 12. __ 13. __ 14. __ 15. __ 16. __ |
1. 5.
10. 12. 14.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

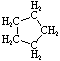

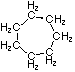

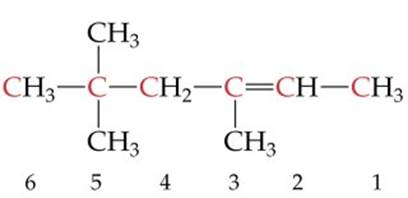
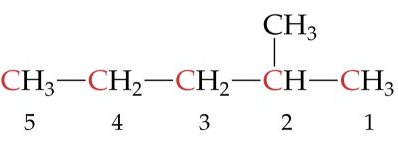
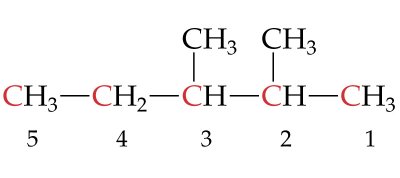
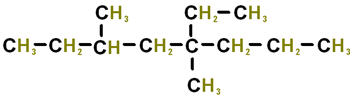
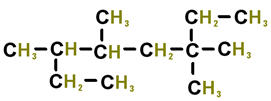
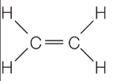

 8.
8.
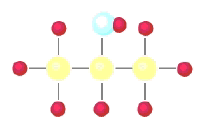 9.
9.

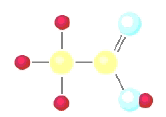
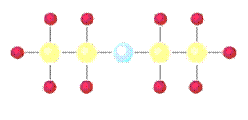
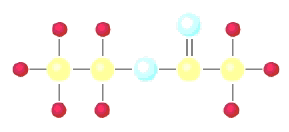
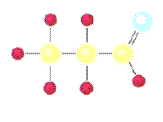

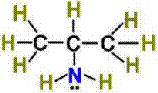 16.
16.