Chapter
5:
The Atomic Nucleus
Part
A: Natural Radioactivity
Part B: Nuclear Particles
Part C: Nuclear Reactions
Part D: Half Life
Part E: Induced Radioactivity
Part F: Nuclear Fission
Part G: Nuclear Fusion
Part H: Isotope Dating of Materials
Part
V: Chapter
5 Vocabulary p154
Part M: Chapter 5 Multiple Choice
(Blackboard - Course Content
-Required Path 2 MC Quizzes – Chapter 5)
Part Z: Conceptual Chemistry Spotlight: Flacking for Shale Gas p159-161
Part
A: Natural Radioactivity

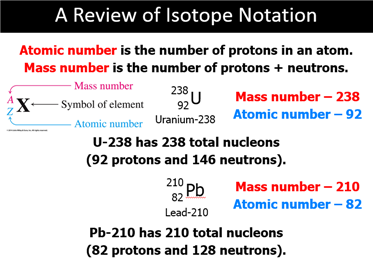

Part
B: Nuclear Particles
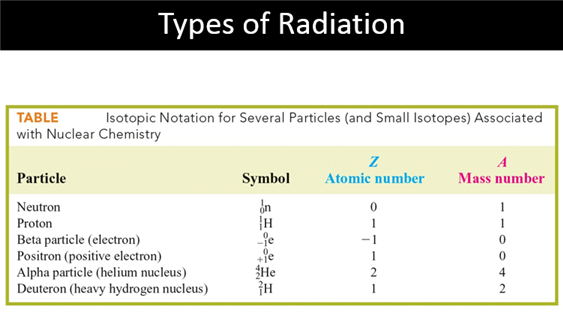
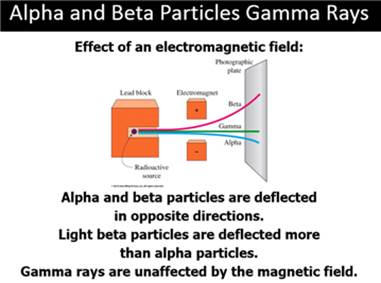
Part
C: Nuclear Reactions
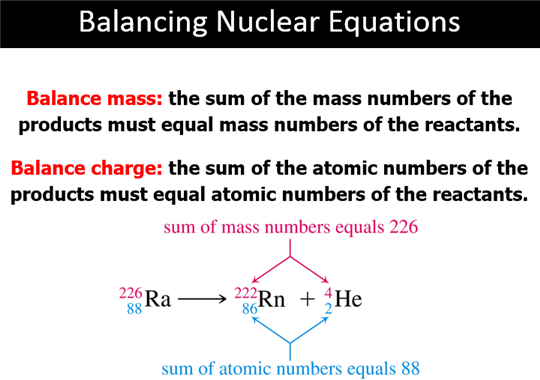




Electron Capture is opposite Beta Radiation
How
is an electron emitted from the nucleus when only
protons and neutrons are present in the
nucleus?
Positron same as Beta; Neutron less than Beta

Part D: Half Life


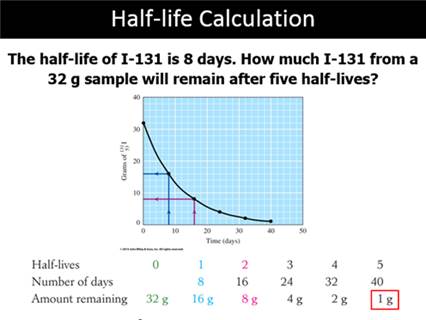
Half
Life: I131 is 8 days; C14 5730 years

Part
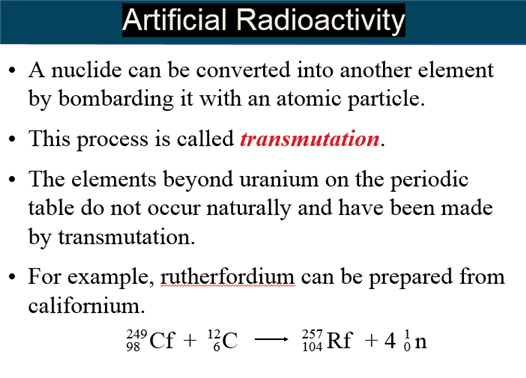
E: Induced Radioactivity





Part F: Nuclear Fission
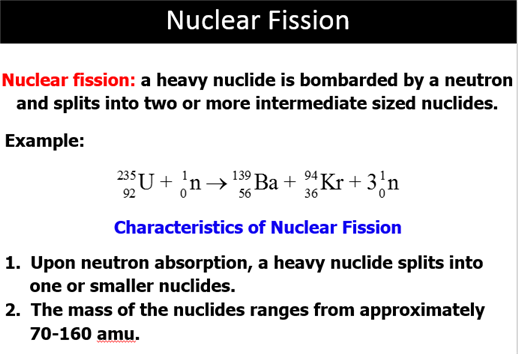


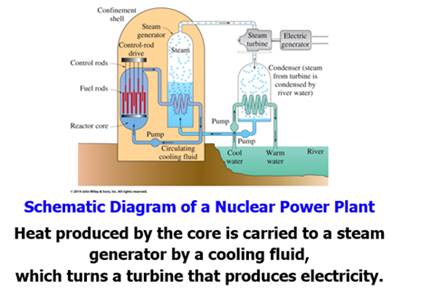
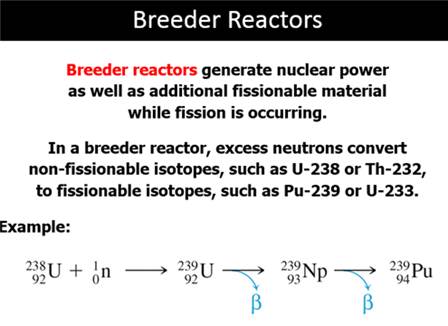


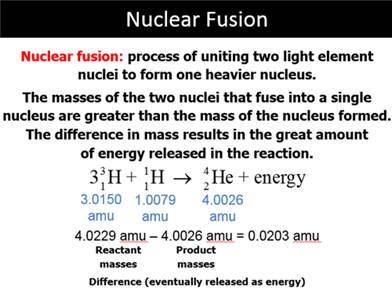
Part
G: Nuclear Fusion



Part H: Isotope Dating of Materials


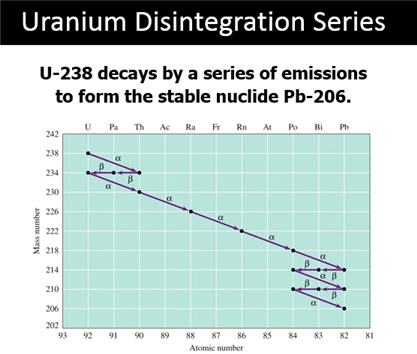

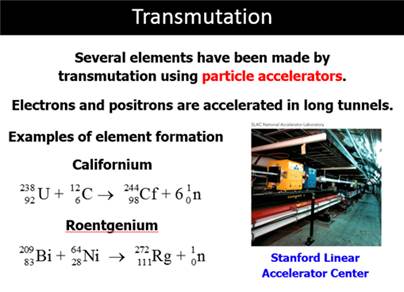



Part
V: Chapter
5 Vocabulary p154
Chapter 5 Vocabulay
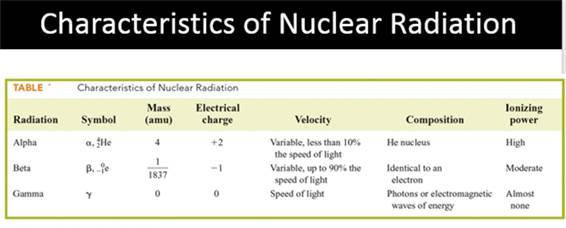
Alpha Particle A subatomic particle consisting of the combination
of two protons and two neutrons ejected by a radioactive nucleus. The
composition of an alpha particle is the same as that of the nucleus of a helium
atom.
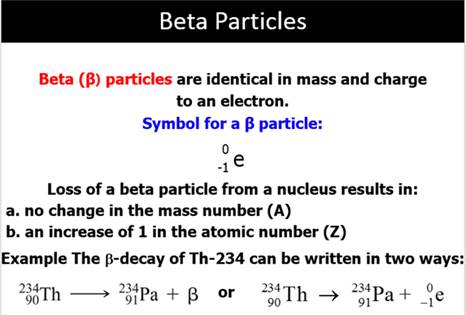
Beta Particle An
electron emitted during the radioactive decay of a radioactive nucleus.
Carbon-14
Dating The
process of estimating the age of once-living material by measuring the
amount of radioactive
carbon-14 present in the material.
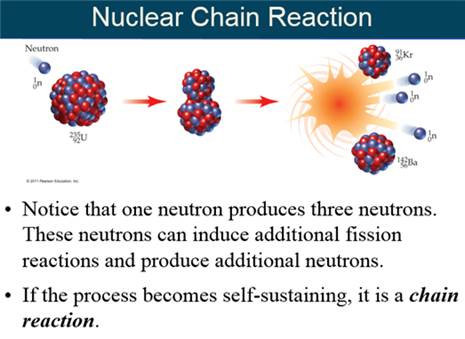
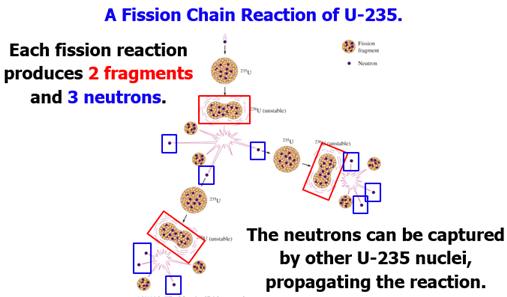
Chain
Reaction A
self-sustaining reaction in which the products of one reaction event initiate
further
reaction events.
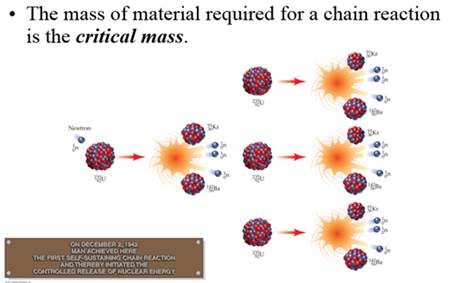
Critical
mass The minimum mass of fissionable material needed
for a sustainable chain reaction.
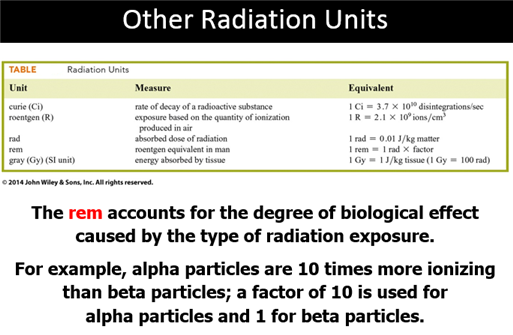
Curie – unit expressing the amount of radioactivity by an element
measuring
3.7 x 1010 disintegrations
per second
Electron Capture – A heavy charged unstable nucleus attracts an
electron which combines with a proton
forming a neutral neutron, decreasing the
atomic number of the element by one.
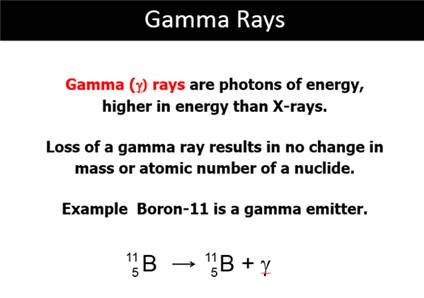
Gamma Rays
High-frequency electromagnetic radiation emitted by radioactive nuclei.
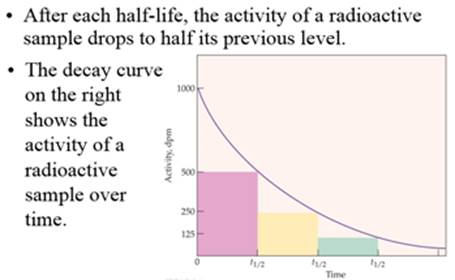
Half-Life The time required for half the atoms in a
sample of a radioactive isotope to decay.
Nuclear
Fission The
splitting of the atomic nucleus into two smaller halves.
Nuclear Fusion - The
combining of nuclei of light atom to form heavier nuclei.
Positron – A subatomic
particle with the mass of an electron, but a positive one charge.
Radioactive – Material containing
nuclei that are unstable because of less than optimal
balance in the number of protons and neutrons
in the nucleus.
Radioactivity – The high-energy
particles and electromagnetic radiation emitted by
a radioactive
substance.
Rem – A unit for measuring the
ability of radiation to harm living tissue
Strong Nuclear Force – The attractive
force between all nucleons, effective only at a short distance.
Thermonuclear fusion –
Nuclear fusion brought about by high temperatures.
Transmutation – The changing
of the atomic nucleus of one element into the atomic nucleus of
another element through a decrease or increase
in the number of protons