CHM1025C
Module Homework Packet Name:___________________
Module 1i: Matter and States of Matter (Chapters 1 & 3)
A. _____(01) Matter Chart- Section 1.4 p8 Fig 1.7 Answers
A1.____ (01) Matter Chart Applications Answers
B. _____(04) Element-Symbol- Section 3.1 p47 Table 3.3 Answers Fig 3.4 Tabl 3.2
B1._____(01) Element Identification Homework/Mixer (Click on Element for Answer)
C. ______(01) Element Classification- Section 3.2 p49 Fig 3.5 Answer
C1.____ (02) Compounds and Chemical Formulas Section 3.3 Answers
_______(10)
Module 1i Total (First Exam)
Module 1ii: Matter and States of Matter (Chapter 4)
D1,____ (02) Chemical and Physical Properties Section 4.1 Answers
D. _____(02) Chemical/Physical/Nuclear Change Sec 4.2 Answers Fig 3.1 Fig 3.6 Fig 3.11 Fig 3.12
E.
_____(01) Forms
of Energy Sec 4.4/lecture Answers Fig 3.13 Fig 3.14 Fig 3.15 Fig 3.16
E1.____ (01) Energy Transformations LectureSee Practice/Concept Exercise Answers
F. _____(03) Phase Diagram (From Lecture) Answers
F1.____
(01) Phase Diagram Applications
_______(10)
Module 1ii Total (Second Exam)
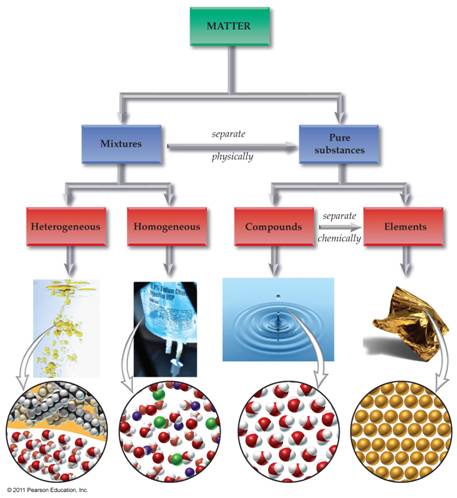
Module One: Part A Matter Chart 01 points
Draw below a matter
chart similar to the chart in section 3.1
page 47 of the Hein Foundations Chemistry
text or it may be of your own design as long as it clearly denotes lines which
describe which words are subunits of the more general word. The chart should include the following: homogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous
mixtures, Matter, Pure Substances, Mixtures, Compounds, Elements, Solutions,
Atoms, Molecules/Formula Units, and Colloids/Suspensions. Also draw/label the arrows: Separate
Physically and Separate Chemically:
Matter Chart Homework Critical Thinking:
Module
One: Part A1 Matter Chart-Critical Thinking Application 1
point
1. Where would you
place: colloids in the matter chart?
2. If you subdivided Inorganic Compounds and Organic
Compounds under compounds.,
sketch below where would you put: Salts, Acids, Bases, Covalent
Compounds?
3. Sketch below and show under which subdivision would you put:
Electrons, Protons, and Neutrons
4. . Sketch below and
show under which subdivision would you put:
electrons, protons,
neutrons, nucleus, orbitals
Module One
Homework Packet
Module One Homework
Packet
M-1 Part B:
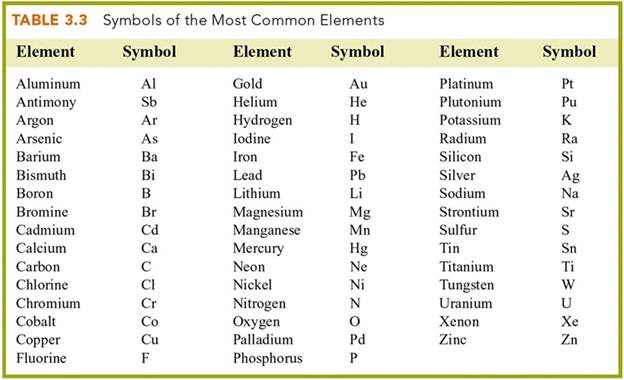
Element/Symbol 4 points
In the blanks below, write the symbol
for the element listed (1/2 pt each), or write the name (with correct spelling)(1 points each) for the element represented by its symbol:
1. Magnesium _____ 21. Cl __
___________
2. Manganese _____ 22. F _____________
3. Tungsten _____ 23. I _____________
4. Platinum _____ 24. Br _____________
5. Gold _____ 25. Zn _____________
6. Silver _____ 26. H _____________
7. Iron _____ 27. O _____________
8. Tin _____ 28. N _____________
9. Helium _____ 29. C _____________
10.
Antimony _____ 30. K _____________
11.
Lead _____ 31. P _____________
12.
Argon _____ 32. B _____________
13. Neon _____ 33. Al _____________
14. Krypton _____ 34. Cr _____________
15. Arsenic _____ 35. Ca _____________
16. Mercury _____ 36. Bi _____________
17. Copper _____ 37. Sr _____________
18. Cobalt _____ 38. Si _____________
19. Beryllium _____ 39. Ni _____________
20. Selenium _____ 40. Li _____________
CHM
1025C Module One: Element Identification Homework
01points
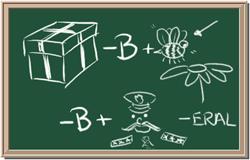
Identify each of the following elements chalk board representation:


1. Element: _______________Symbol:_____ 2.Element: _______________Symbol:_____
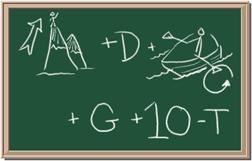
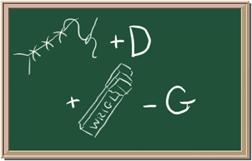
3. Element: _______________Symbol:_____ 4.Element: _______________Symbol:_____

5. Element: _______________Symbol:_____ 6.Element: _______________Symbol:_____
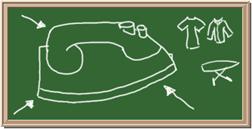
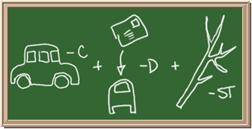
7. Element: _______________Symbol:_____ 8.Element: _______________Symbol:_____

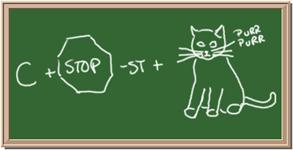
9. Element: _______________Symbol:_____ 10.Element: _______________Symbol:_____
CHM1025C Module One Homework Packet
M-1 Part C: Element Classification 01 points
Using
the periodic chart provided, in the blanks below write the classification of
the elements listed:
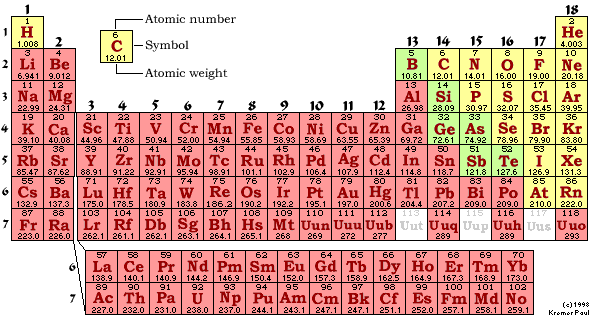
The
classifications of the elements are:
Metals;
Semimetals
(Metalloids);
Nonmetals-Regular;
Nonmetals-Nobel
Gases;
Nonmetals-Class
by Itself
Use
the above classifications to classify each of the following elements.
You
must split the nonmetals into three subclasses:
1. 12C6 ______________
2. 39K19 ______________
3. 11B5 ______________
4. 1H1 _________________
5. 4He2 _________________
6. 56Fe26 _________________
7. 238U92 _________________
8. 73Ge32 _________________
9. 9Be4 _________________
10. 86Rn222 _________________
CHM1025C Module One Homework Packet
Part
C1: Compounds and Chemical Formulas (Section3.4) 2 points
1.
State the Law of
Definite Composition:
2.
Define Molecule:
3.
The chemical
formula for vitamin B3 is: C6H6N2O
In One Molecule How Many:
_____ carbon
atoms
_____ oxygen
atoms
_____ total
atoms
4.
Write the
chemical formula for Vitamin B6 which has eight Carbon atoms, 11
Hydrogen atoms, one Nitrogen atom, and three Oxygen atoms:
How many total
atoms are there in one Vitamin B6 molecule?
5.
Citric Acid (in
citrus fruit) has the following chemical formula:
C3H4OH(COOH)3
In one
molecule of Citric Acid, How many:
______Carbon
atoms
______Oxygen
Atoms
______
Hydrogen Atoms
______ total atoms
How
many atoms are in the following complex ion molecule:
[Cr(N2H4CO)6]4[Cr(CN)6]3 _______atoms
CHM1025C
Module One Homework Packet
Part D: Chemical/Physical/Nuclear Change 2 points
State whether each of the following is a physical change, a chemical change,
or a nuclear change:
__________________1. Electricity
decomposes water.
__________________ 2. Methanol
dissolves in gasoline
__________________ 3. Dry ice pellets
disappear
__________________ 4. Iron oxidizes to
rust
__________________ 5. Bromine vaporizes
into a reddish-brown gas
__________________ 6. Uranium-235
splits into two small elements when bombarded
with neutrons in an atomic bomb.
___________________7. Copper conducts
heat
___________________8. Baking soda
fizzes in vinegar
___________________9. Grinding sugar
crystals into a powder
__________________10. Sodium reacts
with chlorine gas
__________________11. Adding air to a
tire
__________________12. Slicing an orange
into wedges
__________________13. Hydrogen atoms
fuse into helium atoms in a hydrogen bomb
__________________14.” Dry ice”(Solid Carbon dioxide) vaporizes into a gas at room
temperature and sea level pressure
__________________15. Natural Gas burs with a blue flame
CHM1025C
Module One: Sample Exam Homework
Part D1: Chemical/Physical/Nuclear Properties (Section 3.6) 2 points
1. Define: Physical Property:
2. Chemical Property:
3. Classify each of the following as a chemical or physical property:
a.
Color
_________________
b.
Odor
_________________
c.
Reaction with water:
____________________
d.
Solubility in water: ____________________
e.
Melting point: ____________________
f.
Boiling point:
____________________
g.
Sublimation Point: ____________________
h.
Reaction with oxygen
____________________
i.
Density:
____________________
j.
Solid state:
___________________
k.
Reaction producing a Gas: _____________________
l.
Conductor of electricity: _____________________
m.
Water is insoluble in gasoline:
_____________________
n.
Good conductor of heat: _____________________
o.
Two chemical when mixed gives of heat:
___________________
p.
Appearance at Room Temperature: ___________________
q.
An element turns black when heated
___________________
r.
Silver tarnishes in Air ____________________
s.
An element is radioactive: ________________
CHM1025C Module One Homework Packet
Part
E: Energy/Forms of Energy 1 point
Define Energy:
What is the difference
between the two types of energy:
potential and kinetic energy?
List the six different forms
of energy as an energy wheel as stated in the book:
Define the Law of
Conservation of Energy:
Reword the Law of
Conservation of Energy into the first law of thermodynamics:
Which state of matter has the
lowest kinetic energy?
What is the “Heat Death
Theory of the Universe”?
Bonus: define Gravitational
Energy; Tidal Energy; Sound Energy; Magnetic Energy; Radiant Energy; Dark
Energy
CHM1025C Module One Homework Packet
Part
E1: Energy Transformations 1 point
Identify two forms of energy
that are involved in each of the following energy conversions:
1.
relating to a fossil fuel plant:
a. Burning coal converts water to
steam:
b. A turbine spins and drives an
electrical generator:
2.
Solar Hot Water Energy
Panels:
3.
Photovoltaic
Solar Energy Panels:
4.
Radioactive
emissions vaporize water into steam
5.
Identify two forms
of energy that are involved in each of the following devices:
a.
Flashlight
b.
Solar Calculator
c.
Lead-acid battery
6.
Classify the
following energy sources as renewable and nonrenewable:
a. Biomass f. Hydropower
b. Petroleum g.
Coal
c. Geothermal h. natural gas
d. Wind i. solar
e.
Uranium j. propane
CHM1025C Module One Homework Packet
Part
F: Phase Diagrams 3 points
Identify the
points labeled on the
Phase Diagram of water:
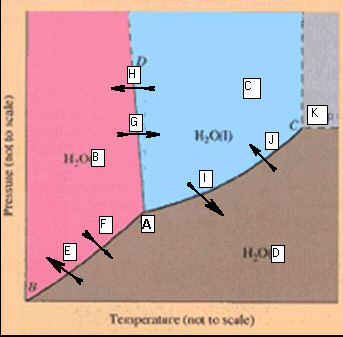
_____________________A.
_____________________B. _____________________H
_____________________C. _____________________I
_____________________D. _____________________J
_____________________E. _____________________K
_____________________F
_____________________G
CHM1025C Module One Homework Packet
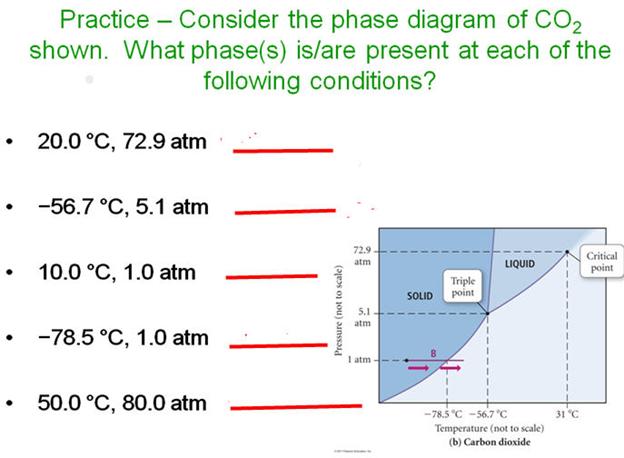
Phase Diagram for Carbon Dioxide.
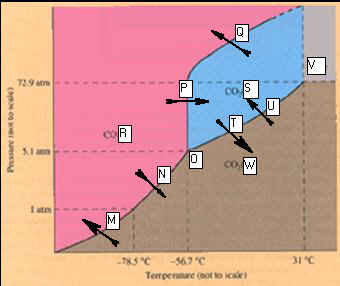
_____________________M.
____________________T
_____________________N. _____________________U
_____________________O. _____________________V
_____________________P. _____________________W
_____________________Q.
_____________________R
_____________________S
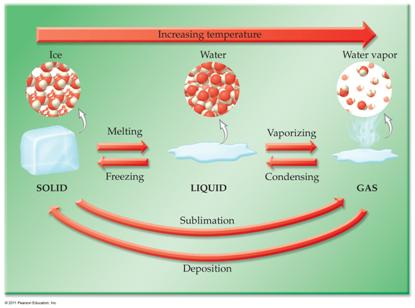
CHM1025C Module One Homework Packet
Part
P1: Phase Diagram Applications
1 point
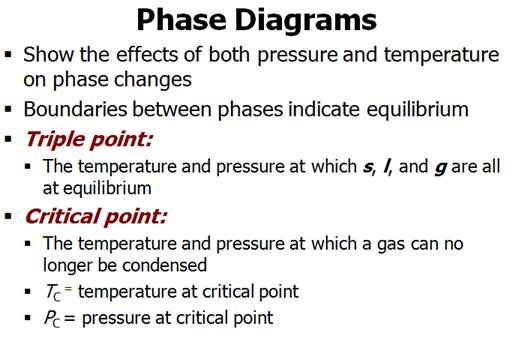

A demonstration of heating
iodine in a beaker has purple vapors..can you explain
using the phase diagram above?