CHM
2045C Name: _________________
Module
5i Homework Packet-Jespersen 7th
Module Five Part I:Chemical
Equations & Stoichiometry (Chap 3-4)
E._____(03) Basic Reaction
Symbols-Chapter
3 Section 3.1 Answers
ef
E1.____(02) Classifying Chemical Reactions- Section 3.1-Lecture
F._____(05) Balancing Chemical
Equations -Sections
3.1 Answers
ef
G._____(05) Predicting Single
Replacement Products Sections 4.8 Answers
H._____(05) Predict Double Replacement
Sections 4.1, 4.3, 4.5 Answers h
H1____
(05) Neutralization/Gas Forming Reactions Section
3.8-3.9-4.5 Lecture
Answers
______(25) Total
= ______%
M-5i Required
Homework:
______(30) M-5i
Pretest Hardcopy Homework Packet
______(30) M-5i Multiple Choice (MC) Homework/Exam (Blackboard
Online)
Evidence for
Chemical Reactions
There are four observations that indicate a
chemical reaction is taking place:
1.
A gas is produced.
Gas may be observed in
many ways in a reaction from light fizzing to heavy bubbling.
2.
An
insoluble solid is produced
in a solution.
a. A substance
dissolves in water to give an aqueous solution.
b. If we add
two aqueous solutions together, we may observe the production of a solid
substance.
c. The
insoluble solid formed is called a precipitate
3. A permanent color change is observed.
a. Many
chemical reactions involve a permanent color change.
b. A change in
color indicates that a new substance has
been formed
4. An energy change is observed
a. A reaction
that releases heat is an exothermic reaction.
b. A reaction
that absorbs heat is an endothermic reaction.
c. Examples of
a heat energy change in a chemical reaction are heat and light being given off.

Module
Five-Part E Basic Stoichiometry
Definitions 3 points
CHM 2045C Module Five
I Homework Packet
Module
Five-Part E Basic Stoichiometry
Definitions 3 points
Fill in the
following with the symbols used in chemical equations which has the stated
translation or meaning(s) :
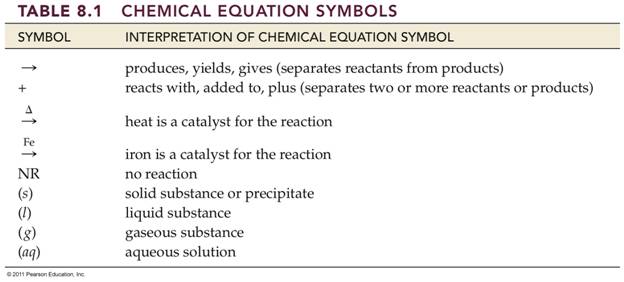
_________1.
Produces, yields, gives
_________2.
Reacts with, added to, plus
_________ and _________ 3. Solid substance or precipitate forms
_________and _________4. Gaseous substance formed
_________5.
Liquid Substance
________5a. Water or aqueous solution
_________6. Reversible Reaction
_________7.
No Reaction
8. Show the
symbol for heat:__________
9. How
would you show a catalyst in a chemical reaction where A plus B forms products
D and E, but is catalyzed by substance C
A +
B à D
+ E
10. Define
Catalyst (See Section 7.2 page 191)
Reference:
Jespersen 7th Chapter 3 Section 3.1
M-5i Homework Packet
Module 5 E1: Classification of Chemical
Reactions 2 Points
(Sections 3.1)
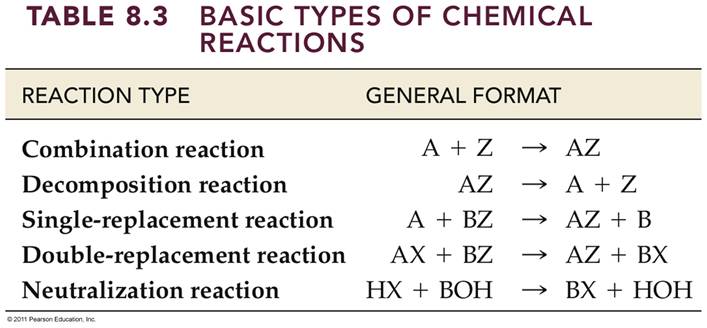
Classify Each of the
following (unbalanced) chemical reactions as:
- Combination
(or synthesis)
- Decomposition
(or Anaylsis)
- Single
Replacement
- Double
Replacement (Precipitation)
- Double
Replacement (Neutralization)
- Double
Replacement (Gas Forming)
______1. Fe
+ FeCl3 à FeCl2
____2. HCl + Mg(OH)2 à MgCl2 +
HOH
_____3. Mg +
HNO3 à Mg(NO3)2 +
H2
_____4. H2 +
N2 à NH3
____5.
NaHCO3 + HCl à NaCl
+ CO2 + H2O
____6.
Ca(NO3)2 + K3PO4 à Ca3(PO4)2 + KNO3
____7.
KClO3 à KCl + O2
____8.
Na + H2O à NaOH
+ H2
M-5i Homework Packet
Reference:
Jespersen 7th Chapter 3 Section 3.1
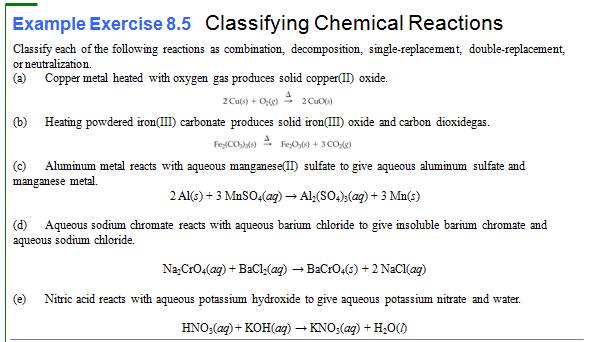
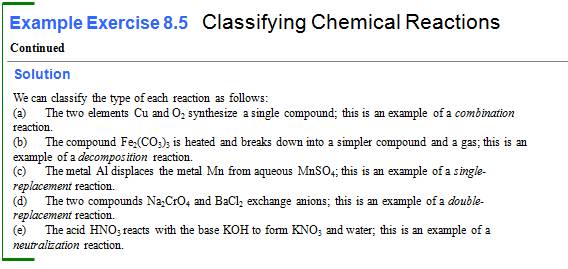
Writing Chemical Reactions (Section 3.1) 1 point
9.
Write a chemical equation or solid cadmium hydrogen carbonate decomposing to yield
solid cadmium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide gas:
10.
Write a chemical equation for the reaction of aqueous solutions of potassium
chromate and calcium sulfate to give the precipitate calcium chromate and
aqueous potassium sulfate.
M-5i Homework Packet

Reference:
McMurry: Section 3.1
Module Five-Part F Balancing Chemical
Equations 5 points
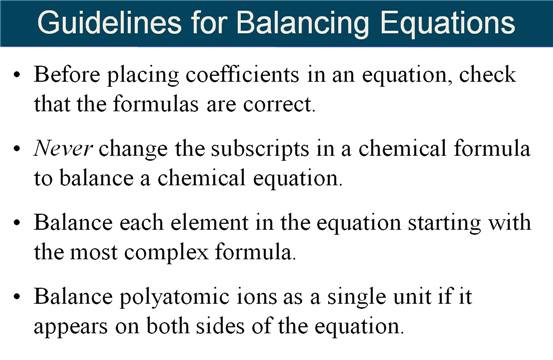


M-5i Homework Packet
Module Five-Part F Balancing Chemical
Equations 5 points
Balance the
following chemical equations (write the chemical formulas in #10 then balance):
1. Fe
+ FeCl3 à FeCl2
2. Al +
O2 à Al2O3
3. Na2CO3 +
C + N2 à NaCN
+ CO
4. FeS +
O2 à Fe2O3 +
SO2
5. IBr +
NH3 à NI3 + NH4Br
6. Cl2 +
HOH à
HCl + HClO
7. AgNO3 à AgNO2 +
O2
8. HClO4 +
P4O10 à H3PO4 +
Cl2O7
9. HCl + Mg(OH)2 à MgCl2 +
HOH
10.
Sodium hydroxide + Hydrochloric
acid à sodium chloride +
water
Reference:
Jespersen 7th Chapter 3 Section 3.1
M-5i Homework Packet
Module Five-Part F Balancing Chemical
Equations

M-5i Homework Packet
Module Five-Part F Balancing Chemical
Equations Continued
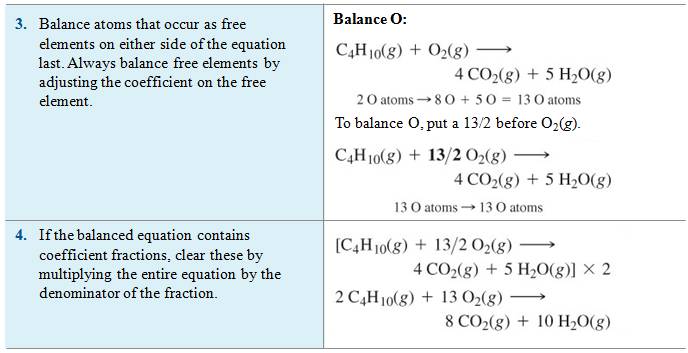
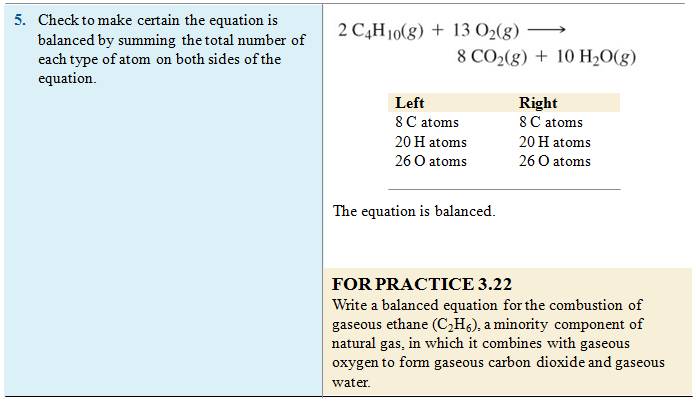
Reference:
McMurry: Chapter 3 Section 3.1
You
may check your work using the online chemical equation balancer at: http://people.emich.edu/bramsay1/ccc-release/chem.html
Reference:
Jespersen 7th Chapter 3 Section 3.1
M-5i Homework Packet
Part
G Single Replacement Reactions 5 points
Given
the following Activity Series:
Li
> K > Ba > Sr > Ca > Na > Mg > Al > Mn > Zn > Fe
> Cd > Co > Ni >
Sn
> Pb > (H) > Cu > Ag > Hg > Au
Given
the following Active Metals:
Li
> K > Ba > Sr > Ca > Na


M-5i Homework Packet
Part
G Single Replacement Reactions
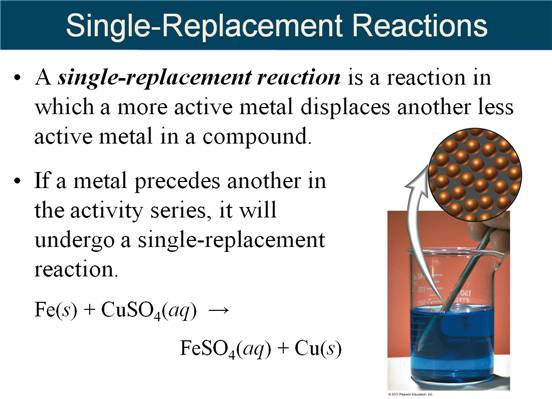

M-5i Homework Packet
Part G Single Replacement Reactions

If you were to (H2O) in the activity
series like an acid is shown as (H), where would you put it? Show below:
Given
the following Activity Series:
Li > K
> Ba > Sr > Ca > Na >
Mg > Al >
Mn > Zn
> Fe > Cd > Co > Ni >
Sn >
Pb > (H)
> Cu > Ag
> Hg > Au
M-5i Homework Packet
Part G Single Replacement Reactions 5 points
Given
the following Activity Series:
Li
> K > Ba > Sr > Ca > Na > Mg > Al > Mn > Zn > Fe
> Cd > Co > Ni >
Sn
> Pb > (H) > Cu > Ag > Hg > Au
Given
the following Active Metals:
Li
> K > Ba > Sr > Ca > Na
Complete
the products of the following reactions, then balance the equation (If no
reaction write NR):
1. Cu (s) + Al(NO3)3 (aq) à
2. Al (s) +
Cu(NO3)2 (aq) à
3. Au (s)
+ H2SO4
(aq) à
4. Ca (s) +
H2O (l) à
5.
Mn (s) + H2O (l) à
Reference:
Jespersen 7th Sections 4.8
M-5i Homework Packet
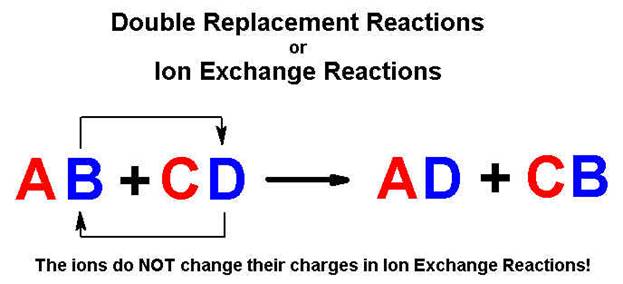
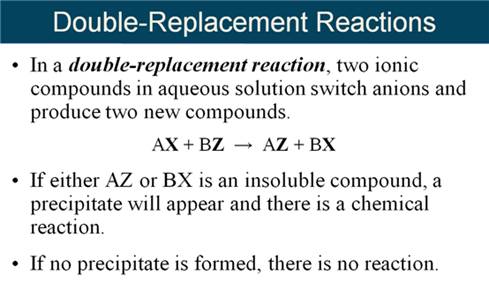

Part H
Double Replacement Reactions 5 points
Given the following Solubility Rules for Ionic
Compounds:
Compounds containing the following ions are
generally soluble in water:
1. Alkali metal ions and ammonium ions, Li+ , Na+ , K+ , NH4+
2. Acetate ion, C2H3O2-
3. Nitrate ion, NO3-
4. Halide ions (X), Cl- , Br-
, I- (AgX, Hg2X2 ,
and PbX2 are insoluble
exceptions)
5. Sulfate ion, SO4 2-
(SrSO4, BaSO4
, and PbSO4 are
insoluble exceptions)
Compounds containing the following ions are
generally insoluble in water:
6. Carbonate
ion,CO32- (see rule 1
exceptions which are soluble)
7. Chromate
ion CrO42- (see rule 1 exceptions which are soluble)
8. Phosphate ion PO43-
(see rule 1 exceptions which are soluble)
9. Sulfide
ion, S2- (CaS, SrS, BaS, and rule 1
exceptions are soluble in water)
10. Hydroxide ion, OH- [ Ca(OH)2
, Sr(OH)2 , Ba(OH)2 , and rule 1 exceptions are soluble)
Complete and balance the following reactions using
the above solubility table (write no reaction or NR if both products are
soluble or a covalent compounds is not formed)
1. AlCl3
(aq) + K2CO3 (aq) à
2. NiSO4
(aq) + Li3PO4 (aq) à
3. NaCl
(aq) + AgNO3 (aq) à
4. H2SO4
(aq) + NaOH (aq) à
5. H3PO4
(aq) + Ba(OH)2 (aq) à
Reference:
Jespersen 7th: Sections
4.1, 4.3, 4.5
M-5i Homework Packet
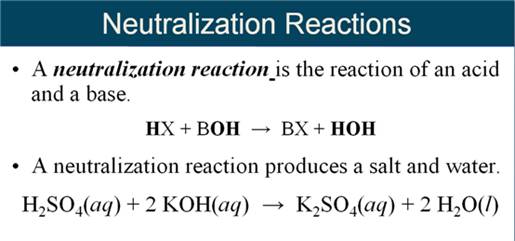
Part H1 Double Replacement Reaction:
Neutralization/Gas Forming
Reactions 5 points
Complete and balance the following precipitation
reactions using the above solubility table
(write no reaction if both
products are soluble or a covalent compounds is not formed)
1. Mg(OH)2 (s)
+ H2SO4
(aq) à
2. H3PO4
(aq) + KOH (aq)
à
3. NH4NO3
(aq) + Ba(OH)2 (aq) à
4. HBr (aq) + Pb(CO3)2 (aq) à
5. LiOH
(aq) + H3PO4 (aq) à
6. Na2CO3
(aq) + HCl (aq)
à
Note for M-5H1:
Neutralization ion Exchange Reaction:
1. When an acid
reacts with a base, salt plus water are the products
Gas Forming Ion Exchange Reactions:
2. When either H2SO3;
H2CO3 or NH4OH is formed as a product it
immediately
decomposes thus demonstrating a gas forming
reaction.
3. Most books do not
show either H2CO3 or NH4OH as products, just
the
decomposed products of the
gases and water in the answer.
If H2CO3
is a predicted product in ion exchange, it is written as
CO2 and H2O.
For example:
Na2CO3
(aq) + HCl (aq)
à [H2CO3](aq)
+ NaCl (aq)
Should
be written:
Na2CO3
(aq) + HCl (aq)
à CO2(g) + H2O
(l) + NaCl (aq)
Two
other products which are shown differently:
[NH4OH] à NH3 + H2O
[H2SO3 ] à SO2 + H2O
Reference:
McMurry: Section 3.1;
Jespersen
7th: Chapters 3 & 4Sections
3.8-3.9-4.5